Figure 2: Treatment with YTX-7739 promotes a terminal UPR response and sensitizes to TMZ and radiation.
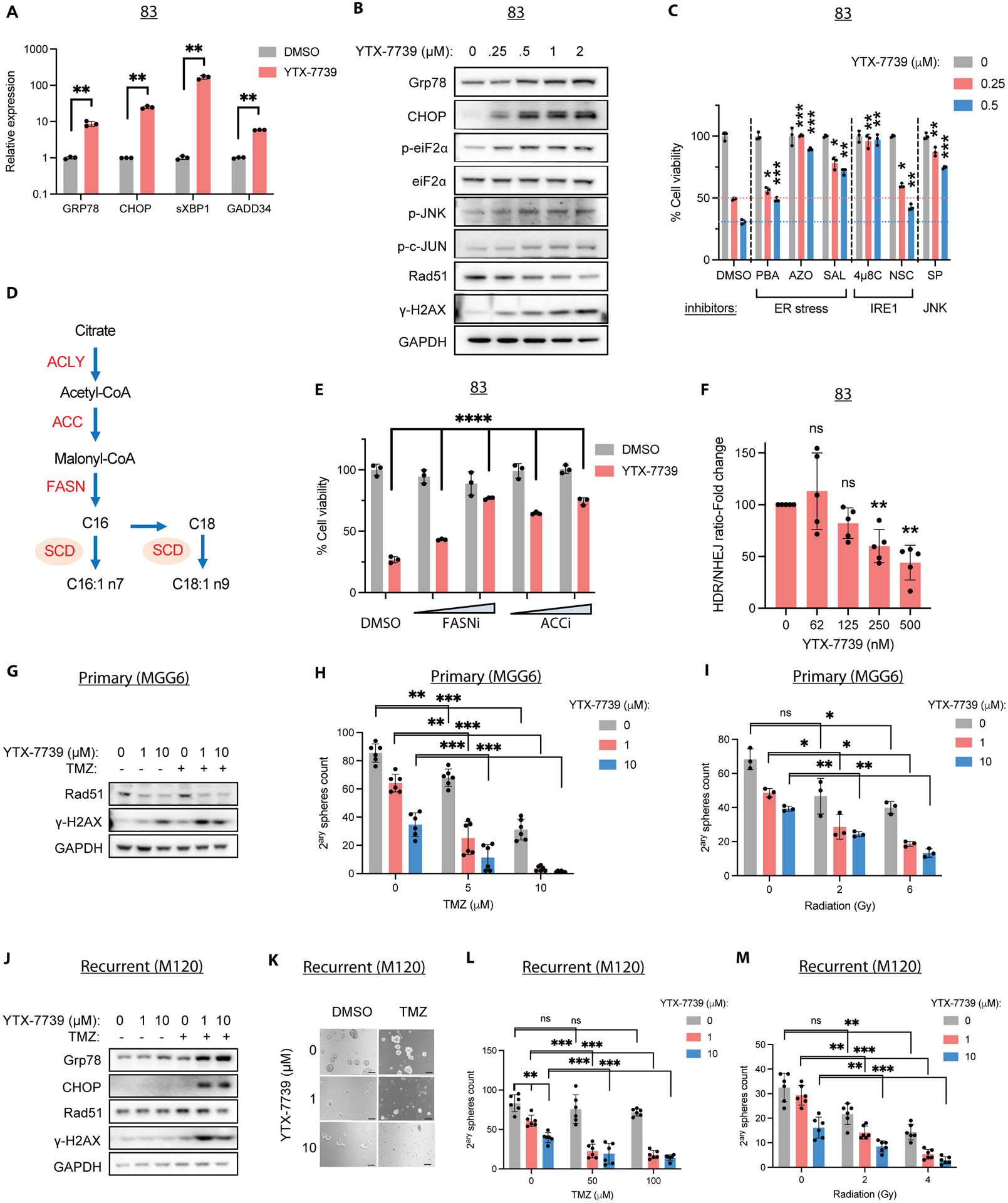
(A) Relative mRNA expression as compared to DMSO (control) and (B) immunoblot analysis of ER stress markers in 83 treated with YTX-7739 for 48h. (C) Cell viability of 83 treated with YTX-7739 in combination with inhibitors of ER stress (PBA: 4mM; Azoramide: 50μM; Salubrinal: 25μM), IRE1 (4μ8C: 25μM; NSC95682: 20μM) and JNK (SP600125: 20μM) for 96h. (D) Overview of de novo lipid synthesis (DNLS) pathway. (E) Cell viability of 83 treated with YTX-7739 (0.5μM) in combination with inhibitors of FASN (GSK2194069: 25–50nM) or ACC (CP-640186: 2.5–5μM) for 96h. (F) Fold-change in HDR/NHEJ normalized to cell viability in 83 treated with YTX-7739. (G-I) MGG6 were pretreated with YTX-7739 followed by TMZ or RT. (G) Immunoblot analysis of DNA repair and damage at 72h after treatment with YTX-7739 and TMZ (5μM). (H-I) Secondary sphere count 9 days after co-treatment with TMZ (H) or RT (I). (J-M) M120 were pretreated with YTX-7739, followed by TMZ or RT. (J) Immunoblot analysis after treatment with YTX-7739 and TMZ (100μM). (K) Representative micrographs of neurospheres. Scale bar, 100μm. (L-M) Secondary sphere count after co-treatment with TMZ (H) or RT (I). ****P<0.0001; *** P<0.001; **P<0.01; *P<0.05
