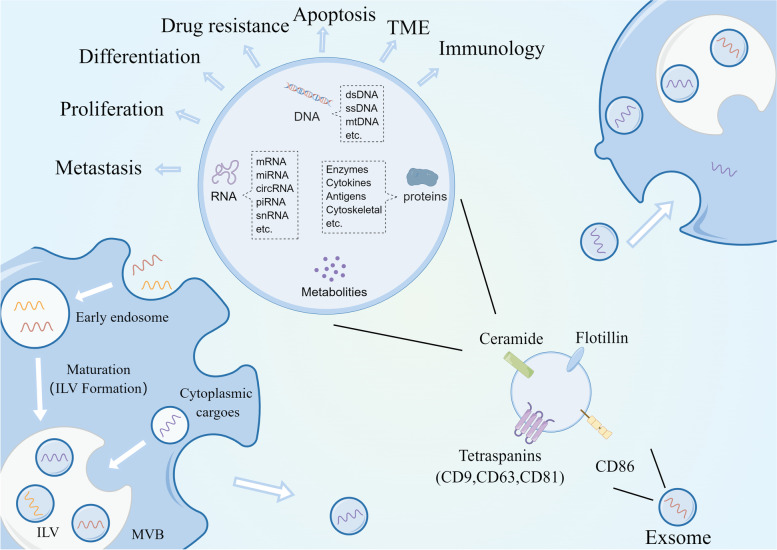
Fig. 4.
Exosomal biogenesis and regulatory mechanisms. The cell membrane wraps specific cellular material inward to form EEs which mature into MVBs. Meanwhile, MVBs also receive specific cargo from the cytoplasm. Different materials within the MVBs are separated by the membrane to form ILVs. Low-cholesterol MVBs are degraded, while high-cholesterol MVBs fuse with the cell membrane to release ILVs into the circulation. The released ILVs are called exosomes. The exosomes are enriched with cell surface proteins on the membranes such as Tetraspanins (CD9, CD81, CD63), CD86, integrins and ceramide, which are used as exosome markers and recognized by target cells. It is reported that exosomes regulate tumor differentiation, proliferation, apoptosis, EMT, drug resistance, and the TME by transmitting intercellular messages