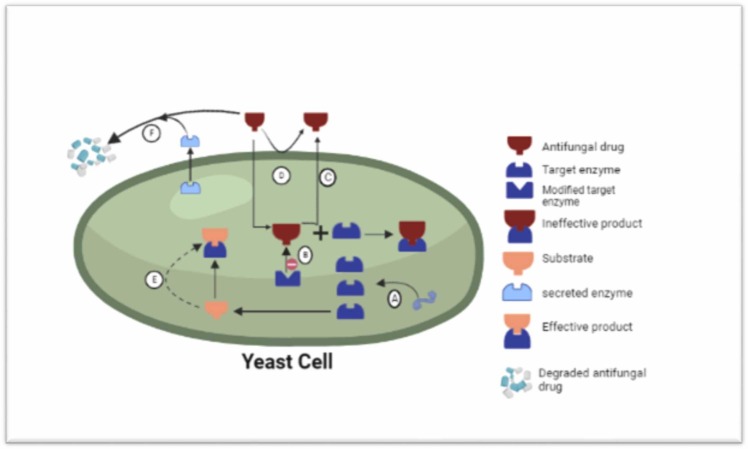
Fig. 3.
Fungal resistance against antifungal compounds. (A) Fungi likely increase the production of enzymes that are main targets for the drugs. This counters the inhibition of metabolic activities. (B) Modifying the spatial structure of target enzyme minimizes the drug binding efficiency. (C) Efflux pumps efficiently pumps out the antifungal drugs out of the cell. (D) fungal cell wall/membrane blocks the penetration of antifungals. (E) The fungal cell escapes the routine pathway that the drug recognizes to target. (E) The secretion of extracellular enzymes having the ability to degrade the antifungal drug.