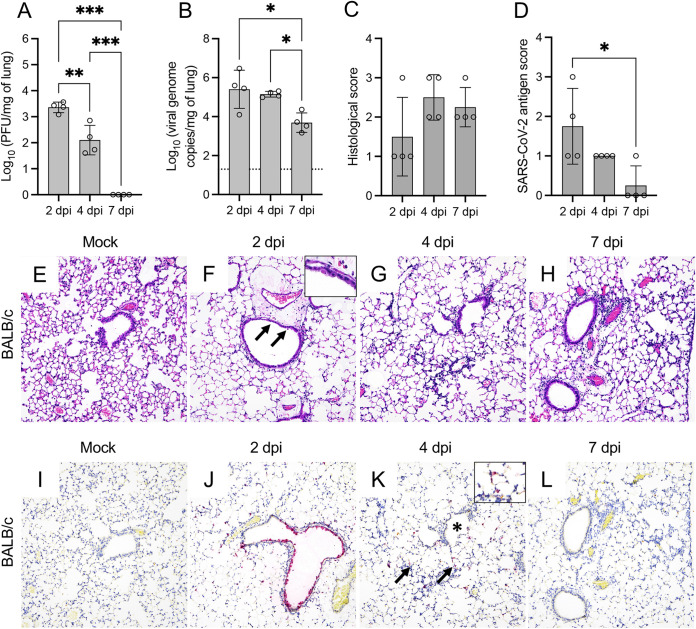
FIG 4.
SARS-CoV-2 MA10 induces injury in the lung of BALB/c mice. Infectious viral particles (A) and viral RNA (B) were quantified in the lung of infected BALB/c mice at 2, 4, and 7 dpi. Histological scores (C) and scoring of SARS-CoV-2 antigen abundance (D) in the lung of BALB/c mice are presented. Bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. Dotted line represents the limit of detection. Temporal histologic lesions (E to H) and viral antigen abundance and distribution (I to L) in the lung of MA10-infected BALB/c mice. There is evidence of bronchiolar degeneration/necrosis at 2 dpi (F, arrows and inset), with abundant viral antigen (J) and mild peribronchiolar inflammation. At 4 dpi, there is evidence of interstitial pneumonia with alveolar septa expanded by mononuclear inflammatory cells, and alveolar spaces contain similar inflammatory cells and karyorrhectic debris (G). Similar histologic changes persist at 7 dpi (H). At 4 dpi, viral antigen is mostly frequent in the cytoplasm of AT2 cells within areas of pneumonia (K, arrows and inset) but spare the bronchiolar epithelium (K, asterisk). Viral antigen is rarely detected at 7 dpi (L). H&E (E to H) and Fast Red (viral antigen) (I to L); ×200 total magnification. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001.