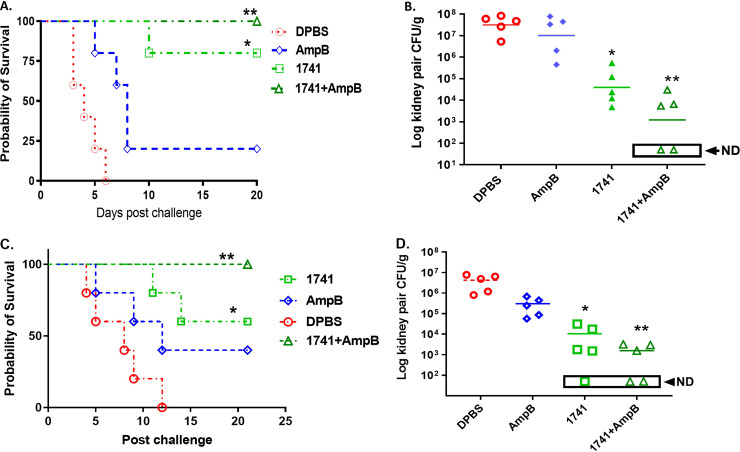
FIG 3.
The antifungal activity of amphotericin B (AmpB) against disseminated candidiasis is enhanced in the presence of human IgGs (IVIG). We evaluate the in vivo efficacy of combined treatment with AmpB and IVIG batch 1741 containing the highest titers of epitope-specific IgGs. We performed the passive transfer of IVIG batch 1741, AmpB, or AmpB plus batch 1741 to naive mice 12 h after lethal challenge with C. auris AR-CDC0386 (2 × 108 CFU) in A/J mice (A and B) and C. albicans SC5314 (1 × 106 CFU) in immunosuppressed C57BL/6 mice (C and D). (A and B) For the A/J mouse model of disseminated C. auris infection, the group receiving combined treatment with batch 1741 plus AmpB had 100% survival (A) and significantly reduced or nondetectable (ND) CFU in the kidney (B). (C and D) Similarly, in the immunosuppressed C57BL/6 mouse model of disseminated C. albicans infection, the group that received combined treatment with batch 1741 plus AmpB also had 100% survival (C) and significantly reduced or undetectable (ND) CFU in the kidney (C and D). In brief, for Candida invasive infection, 4 groups of A/J mice (female, 5 to 7 weeks of age) or C57BL/6 mice (female, 5 to 7 weeks of age) were treated with DPBS, AmpB (minimal effective dose of 0.5 mg/kg), IVIG batch 1741 (200 μL; 5 mg/mL), or IVIG batch 1741 plus AmpB 12 h after lethal challenge with each Candida isolate as described in the text. The mice were monitored for survival up to 21 days postinfection, and CFU were evaluated in the kidney either when mice succumbed to the disease or at termination on day 21 p.i.