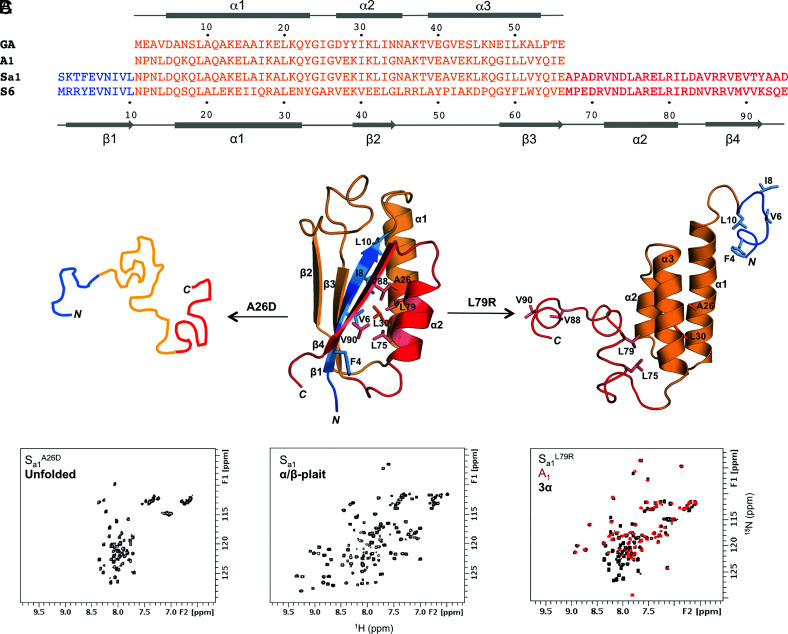
Fig. 1.
Unmasking alternative fold topologies. (A) Sequence alignment of 3α A1 and α/β-plait Sa1, with corresponding secondary structure regions at the Top and Bottom of the alignment. The parent sequences from which A1 and Sa1 are derived, GA and S6 respectively, are also shown. (B) A single amino acid mutation in Sa1 (Center) such as A26D leads to unfolding (Left), while a L79R mutation exposes the alternative 3α state (Right). Color coding is as follows: N-terminal residues 1 to 10 (blue); residues 11 to 66 aligning with the A1 amino acid sequence (orange); C-terminal residues 67 to 95 (red). (C) Representative chemical shift patterns in 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra of the unfolded (Left), α/β-plait (Center), and 3α states (Right). The HSQC spectrum of Sa1L79R (Right, black) is overlaid with the 56-amino acid 3α-helical protein, A1 (red).