Fig. 5.
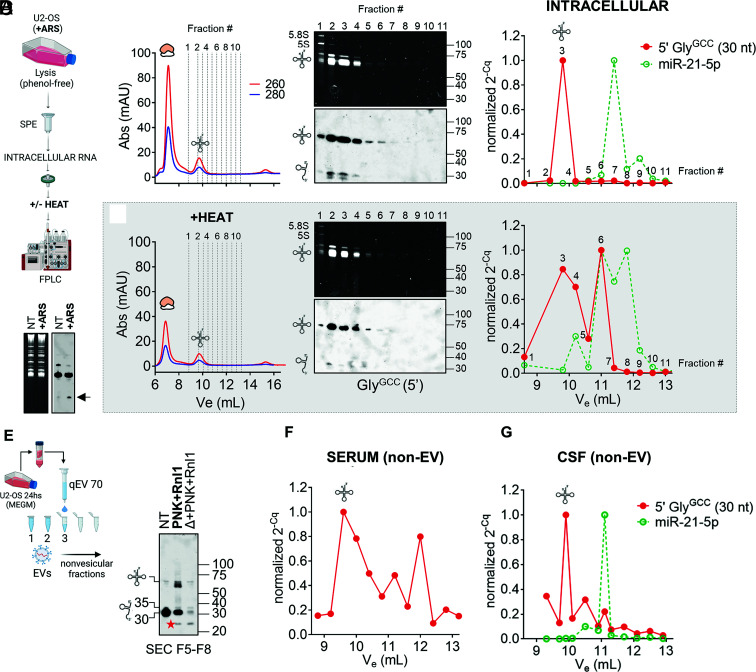
Detection and analysis of nicked tRNAs in intracellular (A–D) and extracellular (E–G) samples. (A) Schematic representation of SEC-based (native) intracellular RNA fractionation as performed in (C) and (D). (B) Northern blot of intracellular RNAs showing the presence of 5′ tRNA halves in arsenite (ARS)-treated samples (i.e., tiRNAs). (C) Purified RNA from ARS-treated U2-OS cells was separated on a Superdex 75 column using an FPLC system. Selected fractions were analyzed by northern blot (Center) or by stem-loop RT-qPCR (Right). Cq values were normalized to the fraction containing the highest signal. (D) Same as in (C), but the RNA was heat-denatured before injection. (E) Cell-conditioned, RI-treated, serum-free medium from U2-OS cells was fractionated with an Izon 70-nm qEVoriginal column to prepare EV-depleted fractions. Northern blot analysis of tRNAs & tDRs in pooled nonvesicular extracellular fractions (F5 to F8) before and after enzymatic repair with T4 PNK and T4 Rnl1. Red star: a ~24-nt band that was only observed in the presence of Rnl1. (F and G) Separation by SEC (as done in C) of purified RNA from Proteinase K-treated ultracentrifugation supernatants of human serum (E) or CSF (F). Selected eluted fractions were analyzed by SL-RT-qPCR using primers specific for 5′ tRNAGlyGCC halves of 30 nt (red) and miR-21-5p (green). A tRNA icon in this figure indicates fractions where full-length tRNAs are expected to elute (if present).