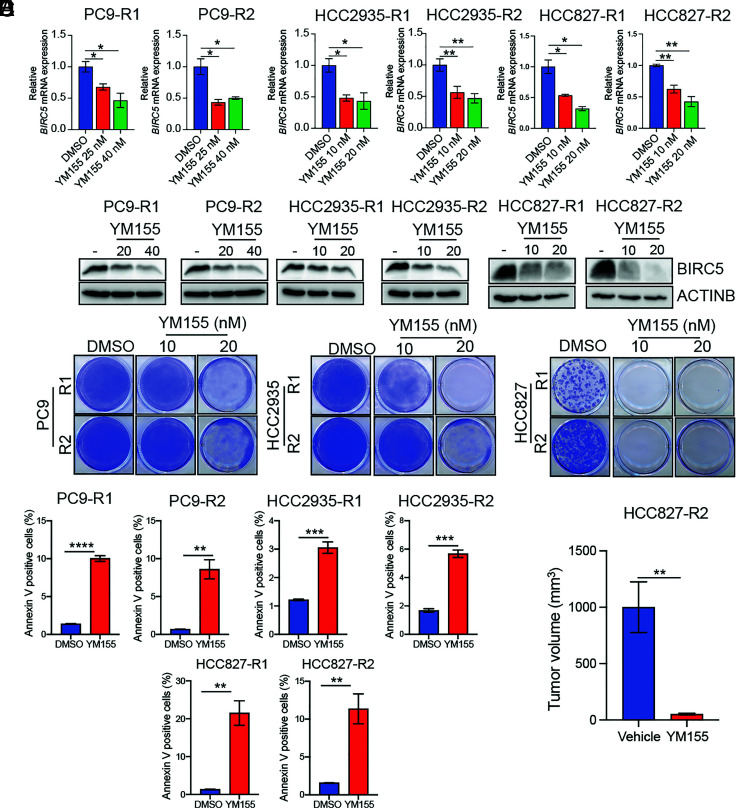
Fig. 6.
The BIRC5 inhibitor YM155 blocks growth of EGFRi-resistant LUAD cells in cell culture and mice. (A) Relative expression of BIRC5 mRNA in the indicated EGFRi-resistant LUAD cell lines treated with DMSO or BIRC5 inhibitor YM155 (10 and 20 nm for HCC827-R1, HCC827-R2, HCC2935-R1, and HCC2935-R2; 20 and 40 nm for PC9-R1 and PC9-R2) for 48 h, as measured by qRT-PCR. (B) Immunoblot analysis measuring expression of BIRC5 in the indicated EGFRi-resistant LUAD cell lines treated with DMSO or YM155 (10 and 20 nm for HCC827-R1, HCC827-R2, HCC2935-R1, and HCC2935-R2; 20 and 40 nm for PC9-R1 and PC9-R2) for 48 h. (C) The indicated EGFRi-resistant LUAD cell lines were treated with DMSO or YM155 (10 and 20 nm), and survival was measured in clonogenic assays. Representative wells for cells grown under the indicated conditions are shown. (D) The indicated LUAD EGFRi-resistant cell lines were treated with YM155 (20 nM for HCC827-R1, HCC827-R2, HCC2935-R1, and HCC2935-R2; 50 nM for PC9-R1 and PC9-R2) or DMSO control for 48 h and then analyzed by FACS-based annexin V-PE staining. (E) EGFRi-resistant HCC827 cells (HCC827-R2) were injected subcutaneously into the flanks of NSG mice (n = 5), and animals were treated with vehicle (0.9% saline) or YM155 (3.5 mg/kg). Average tumor volumes at the end of the experiment are shown. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.