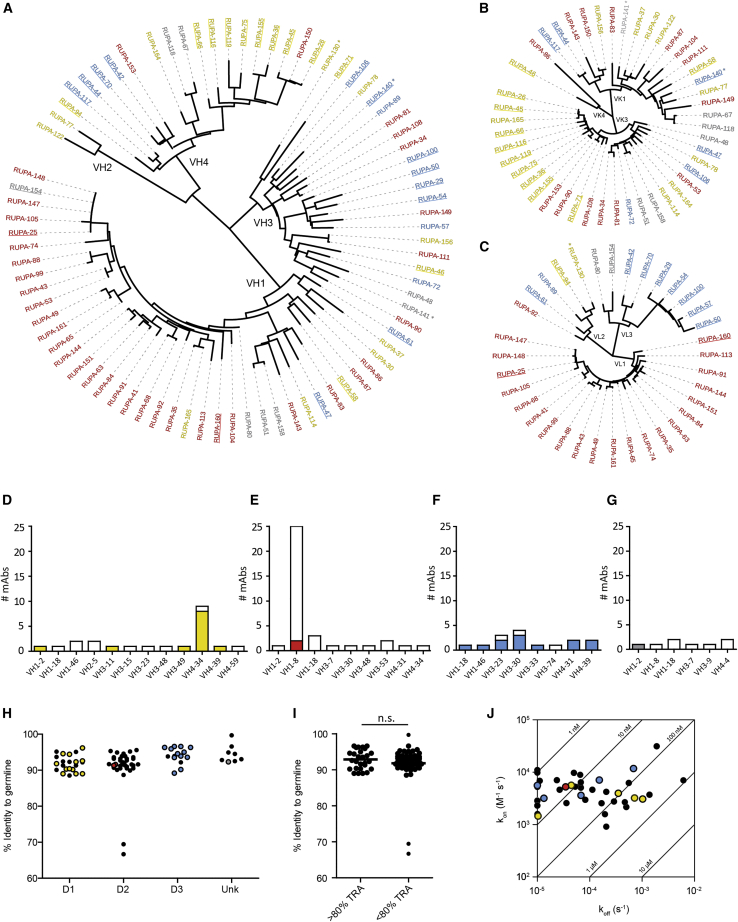
Figure 3.
Pfs48/45-specific mAbs are genetically diverse
(A–C) Phylogenetic trees of (A) VH, (B) VK, and (C) VL chain sequences. mAbs are colored according to domain specificity. Potent mAbs, i.e., >80% TRA in SMFA, are underlined. mAbs from the Ugandan donor are marked with an asterisk.
(D–G) Bar graphs showing the number of mAbs per heavy-chain family for (D) D1-, (E) D2-, and (F) D3-specific mAbs and (G) mAbs with unknown specificity. Colored bars represent mAbs with >95% TRA at 100 μg/mL with the actual color-reflecting domain (as in Figure 1).
(H) Graph showing heavy-chain gene sequence identity to germline sequences. Individual dots represent individual mAbs and are grouped by domain specificity. Colored dots are mAbs with >95% TRA at 100 μg/mL.
(I) mAbs grouped by potency. Groups are compared by Mann-Whitney test. n.s., not significant.
(J) Isoaffinity plot showing binding kinetics as determined by surface plasmon resonance with immobilized antibodies and full-length Pfs48/45 as analyte. Colored dots are mAbs with >80% TRA at 100 μg/mL and are colored by domain specificity. kon, association constant; koff, dissociation constant.