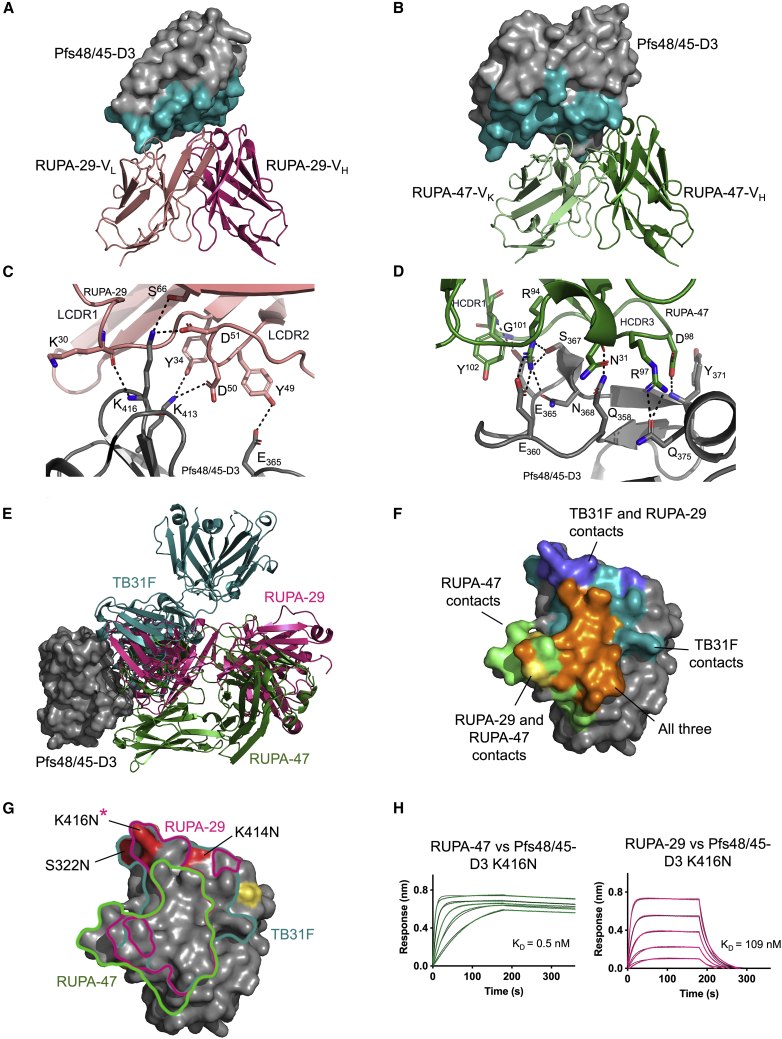
Figure 4.
Delineation of Pfs48/45-D3 epitope Ia recognized by human antibodies
(A and B) Variable domains of (A) RUPA-29 and (B) RUPA-47 bound to Pfs48/45-D3. Pfs48/45-D3 is depicted as the surface with the epitope of TB31F colored in teal.
(C and D) Interactions between Pfs48/45-D3 and RUPA-29 or RUPA-47. RUPA-29, RUPA-47, and Pfs48/45-D3 are depicted as cartoons with residues forming H-bonds and salt bridges (black dashes) shown as sticks. (C) Interactions between LCDRs of RUPA-29 and Pfs48/45-D3. (D) Interactions between HCDRs of RUPA-47 and Pfs48/45-D3.
(E) Structure of Pfs48/45-D3 (gray) bound to RUPA-29 (pink), RUPA-47 (green), and TB31F (teal; PDB: 6E63).
(F) Pfs48/45-D3 in gray with residues that contact only TB31F (teal), only RUPA-47 (green), both RUPA-29 and RUPA-47 (yellow), both TB31F and RUPA-29 (slate), and all three (orange).
(G) Pfs48/45-D3 shown as the surface with the epitopes of RUPA-47 (green), RUPA-29 (pink), and TB31F (teal) outlined. Polymorphisms that do not interact with mAbs are in yellow, whereas those that interact with mAbs are in red and labeled. Polymorphisms that impact antibody binding are indicated with an asterisk.
(H) Biolayer interferometry (BLI) curves of Fabs RUPA-47 and RUPA-29 binding to Pfs48/45-D3 with the K416N polymorphism.
See also Figures S4 and S5 and Tables S3–S5.