Figure 1.
Genetics and binding characteristics of Pfs230-C1 antibodies
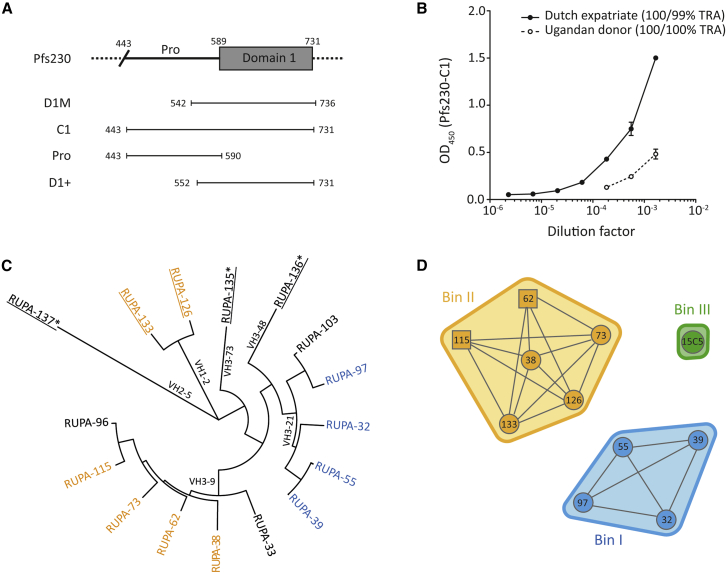
(A) Schematic representation of a fragment of Pfs230, focusing on the pro-domain and first of fourteen 6-Cys domains. Domain boundaries are indicated by amino acid numbers. The leading Pfs230-vaccine construct (D1M14) and recombinant constructs used in this study (C1, Pro, and D1+) are shown below.
(B) Recognition of Pfs230-C1 by plasma samples from two naturally exposed donors in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Values are means of two technical replicates, and error bars represent the SEM. TRAs of purified total IgG, tested at 1:3 dilution in the presence of complement, from both donors are shown in the legend and are outcomes of two independent SMFAs. The raw SMFA data can be found in Table S2.
(C) Phylogenetic tree of heavy-chain gene sequences, generated with MEGA7 software using default settings.16 mAbs that were derived from the Ugandan donor (n = 5) are underlined. mAbs that target the pro-domain are indicated with an asterisk. Names are colored according to competition data in (D), while mAbs without available competition data are shown in black.
(D) Epitope bins were determined by competition experiments and are shown as envelopes. Competition between antibodies was tested in two orientations; one antibody coupled to a chip and the other one in solution, and vice versa. Antibodies with data in two directions are shown in circles and those with data in one direction as squares. Competition data were only available for ten of the C1-specific antibodies. See also Figures S1 and S2.