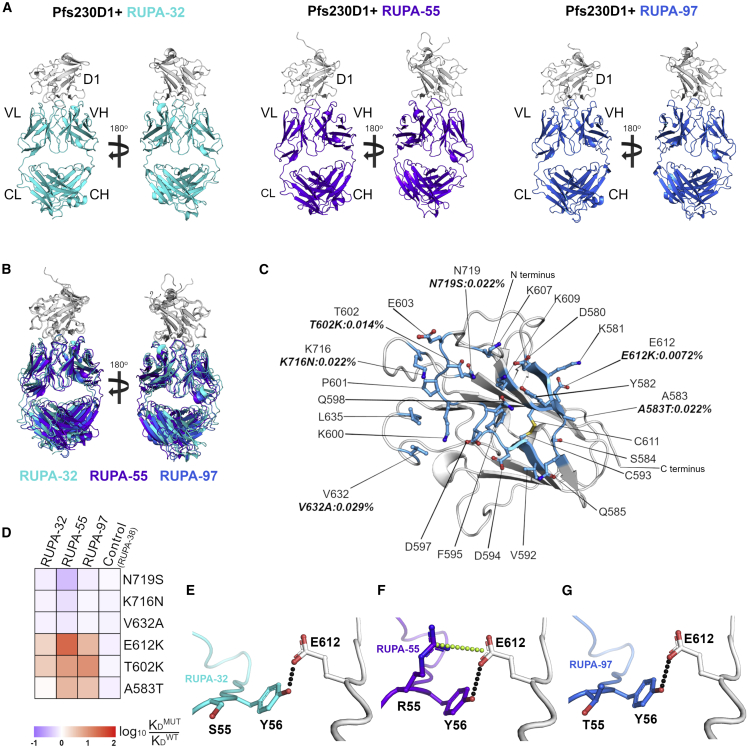
Figure 3.
Structural delineation of a high-potency transmission-blocking epitope on Pfs230 D1+
(A) Overall structures of Pfs230 D1+ (white) bound by Fabs RUPA-32, -55, and -97 (cyan, purple, and blue, respectively).
(B) Superposition of all three Fab-antigen structures from (A) structurally aligned using Pfs230 D1+.
(C) The common epitope on Pfs230 D1+ between all three Fabs colored in marine blue. Epitope residues are labeled, and side chains are shown as sticks. SNPs occurring within the epitope are labeled along with their allele frequency (Table 1).
(D) Relative effect of SNP mutations on the binding constants of Fabs RUPA-32, -55, and -97. RUPA-38 binds to a different epitope on Pfs230 D1+ and was used as a control (Table S5).
(E–G) Hydrogen bonds (black) and a salt bridge (yellow) formed between E612 on Pfs230 and residues on RUPA-32, -55, and -97, respectively. The salt bridge is drawn between resonant charge centers of the arginine and glutamate side chains. See also Figures S3–S5.