Figure 7.
Classified JAK1 missense mutations alter tumor organoid sensitivity to autologous anti-tumor T cells
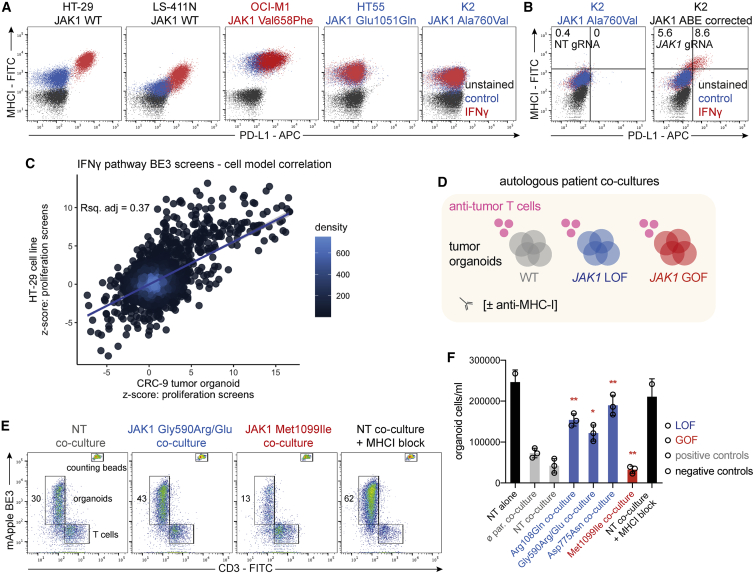
(A) Flow cytometry analysis of PD-L1 and MHC-I expression in response to IFN-γ in cancer cell lines with endogenous, classified LOF or GOF mutations in JAK1.
(B) Flow cytometry analysis of PD-L1 and MHC-I expression after correction of an endogenous JAK1 LOF mutation with ABE8e-NGN in K2 cells. The percentage of cells in each gate is indicated.
(C) Correlation between iBE3 base editing screens in HT-29 cells and CRC-9 tumor organoids. z-scores from the IFN-γ comparison with the control arm were compared for gRNAs targeting the IFN-γ pathway.
(D) Schematic of co-culture experiments to assess T cell-mediated killing of patient-derived, autologous tumor organoids (CRC-9).
(E) T cell-mediated killing of autologous human tumor organoids. Flow cytometry analysis of T cells and organoids (expressing iBE3-mApple) after 72 h of co-culture. The percentage of gated organoid cells is indicated. Counting beads were used to quantify the absolute cell counts.
(F) Quantification of T cell-mediated killing of autologous tumor organoids from flow cytometry analysis. Data represent the average ± standard deviation of three biological replicates and were compared against parental co-culture controls using an unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t-test (∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05). NT, non-targeting gRNA; ø par., parental tumor organoid. All data are representative of two independent experiments performed on separate days. See also Figure S7.