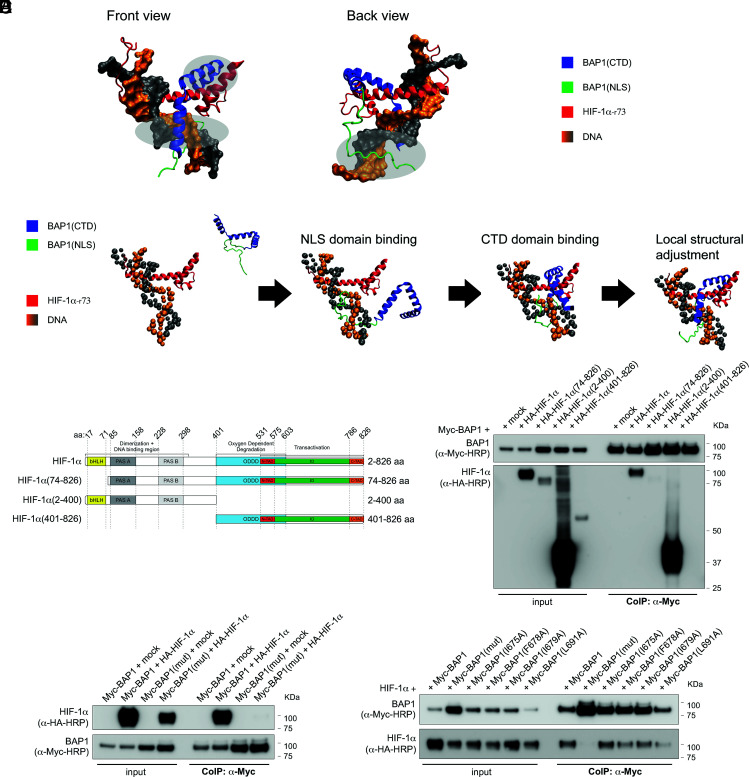
Fig. 3.
The CDT-NLS domain of BAP1 interacts with residues 1 to 73 of HIF-1α. (A) Structural modeling for the binding complex of BAP1(CTD-NLS) and HIF-1α (1-73) (residues 1 to 73 of HIF-1α) in the presence of DNA. The CTD of BAP1 is colored in blue, the NLS domain of BAP1 is colored in green, HIF-1α is colored in red, DNA is colored in orange and grey; three interacting regions are marked by light silver circles. (B) Coarse-grained molecular dynamic simulations to model the binding complex of BAP1(CTD-NLS) and HIF-1(1-73). The NLS domain (colored in green) is extended to increase the searching range of BAP1 to bind to HIF-1α. The NLS domain of BAP1 binds to HIF-1α first. Then the CTD binds sequentially. (C) HA-tagged HIF-1α fragments and HIF-1α domains: basic-helix-loop-helix motif (bHLH) protein, two Per and Sim (PAS) domain (A and B), oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODDD), two transactivation domains (TAD): NH2-terminal (N-TAD) and COOH-terminal (C-TAD), intervening inhibitory domain (ID). (D) BAP1 binds to the N terminus region of HIF-1α [HIF-1α(2-400)]. Residues 1 to 73 of HIF-1α are essential for the interaction because HIF-1α(74-826) did not bind BAP1. CoIP of BAP1 and HIF-1α in homogenates from HEK-293 co-transfected with Myc-BAP1 and HA-tagged HIF-1α or the HA-tagged HIF-1α fragments displayed in (C), or the empty vector (mock); anti-Myc resin was used as bait. (E) Point Mutations of residues I675, F678, I679, and L691 of BAP1 abolish the interaction with HIF-1α. CoIP of BAP1 and HIF-1α in homogenates from HEK-293 co-transfected with Myc-BAP1 or Myc-BAP1(mut) (in which residues I675, F678, I679, L691 of BAP1 are mutated to Alanine), and HA-tagged HIF-1α or empty vector (mock); anti-Myc resin was used as bait. (F) The simultaneous mutation of residues I675, F678, I679, L691 of BAP1 abolish the interaction with HIF-1α, while single-point mutations decrease but do not abolish this interaction. CoIP of BAP1 and HIF-1α in homogenates from HEK-293 co-transfected with HA-tagged HIF-1α and Myc-BAP1, or Myc-BAP1(mut) (in which residues I675, F678, I679, L691 of BAP1 are mutated to Alanine), or Myc-BAP1 mutants carrying each individual point mutation; anti-Myc resin was used as bait.