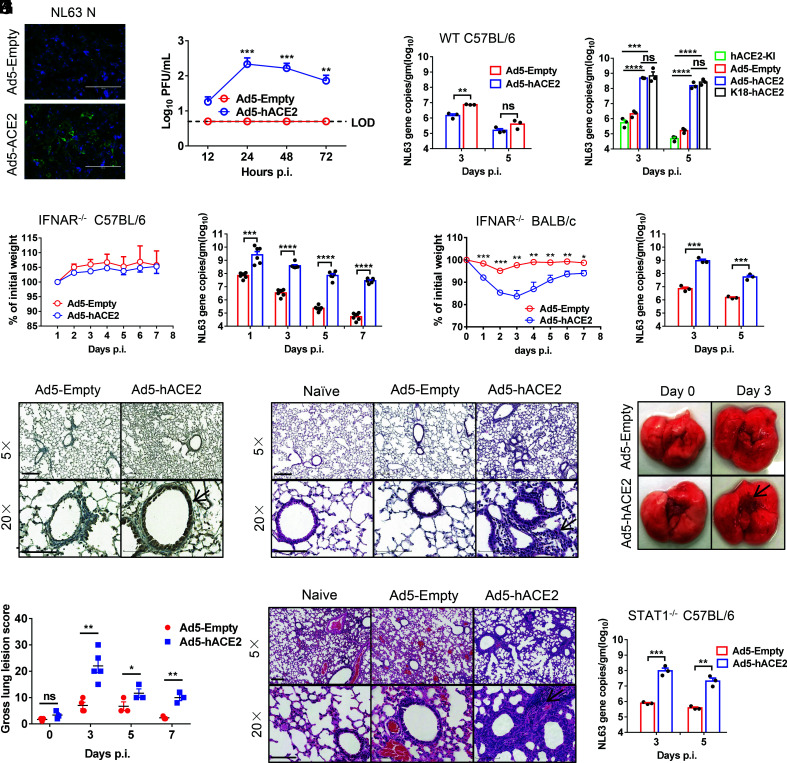
Fig. 2.
Development of mice sensitized to NL63 infection. (A and B) Ad5-hACE2-transduced 17CL-1 cells were infected with NL63 at MOI of 0.02 at 48 h post transduction, and virus antigen was determined by immunofluorescence assays at 48 h.p.i. (A), and virus titers were determined by plaque assay at 12,24, and 48 h.p.i. (B). (Scale bars = 200 µm.) (C) Five days after WT C57BL/6 mice were transduced with 2.5 × 108 FFU of Ad5-hACE2 or Ad5-Empty in 75 μL DMEM intranasally, mice were intranasally infected with 1 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM, lungs were harvested and homogenized at the indicated time points, and the viral load was detected by RT-qPCR. Viral loads are expressed as gene copies /g lung tissue (n = 3 mice per group per time point). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Ad5-hACE2-transduced IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 mice, hACE2 C57BL/6 knockin mice, and K18-hACE2 mice were intranasally infected with 1 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM, lungs were harvested and homogenized at the indicated time points, and the viral load was detected by RT-qPCR. Viral loads are expressed as gene copies/g lung tissue (n = 3 mice per group per time point). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (E and F) Ad5-hACE2- or Ad5-Empty-transduced IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice were intranasally infected with 1.0 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM. Weight changes in 6 to 8-wk-old IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 (E) and BALB/c (F) mice were monitored daily (n = 3 mice per group). To obtain virus kinetics in IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 (E) and BALB/c mice (F), lungs were harvested and homogenized at the indicated time points, and the viral load was detected by RT-qPCR. Viral loads are expressed as gene copies /g lung tissue (n = 3 mice per group per time point). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (G) Three days post infection, lungs were harvested from IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 mice, fixed in zinc formalin, and embedded in paraffin. Sections were stained with mice sera from VRP-NL63-N-immunized mice. Arrowheads indicate regions with NL63 antigen expression. (Bars = 200 and 100 μm, Top and Bottom, respectively). (H and I) Representative HE staining of lungs from IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 (G) and BALB/c (J) mice harvested at 3 d.p.i. Arrowheads indicate regions with interstitial pneumonia with perivascular and interstitial inflammatory cell infiltrates. (Bars = 200 and 100 μm, Top and Bottom, respectively). (J) Photographs of lung specimens isolated from infected IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 mice at indicated time points are shown. Arrowheads indicate regions with vascular congestion and hemorrhage. (K) Gross lung lesion scores are mean ± SE (error bars) and were graded based on the percentage of lung area affected (n = 3 or 4 mice per group per time point). (L) Ad5-hACE2- or Ad5-Empty-transduced STAT1−/− C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with 1.0 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM. Lungs were harvested and homogenized at the indicated time points, and the viral load was detected by RT-qPCR. Viral loads are expressed as gene copies/g lung tissue (n = 3 mice per group per time point). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.005, ***P ≤ 0.0005, ****P ≤ 0.0001).