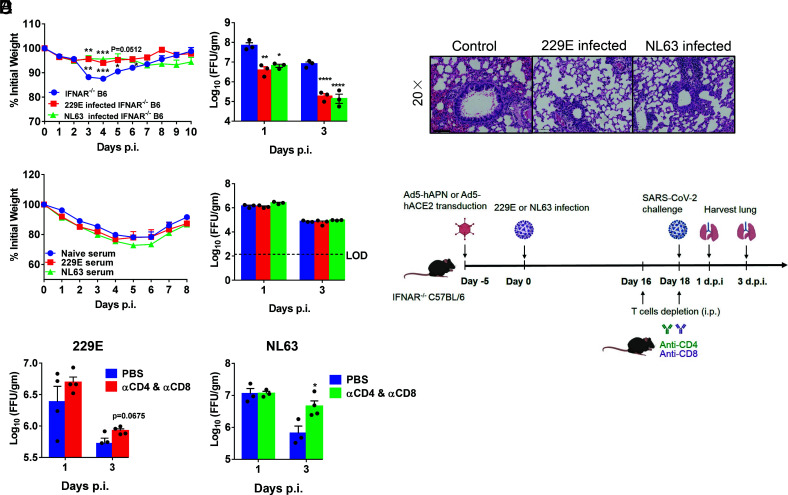
Fig. 6.
HCoV-229E- and NL63-infected mice were partially protected from SARS-CoV-2 infection. (A and B) Ad5-hAPN- and Ad5-hACE2-transduced IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with 1.5 × 105 TCID50 of 229E and 1.0 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM, respectively. Twenty one days postinfection, mice were infected with 5 × 104 PFU of SARS-CoV-2 Beta (B.1.351) variant. Weight changes (n = 4 or 5 mice) were monitored daily, and viral titers in lungs were measured at the indicated time points (A), and hematoxylin/eosin staining of sections of paraffin-embedded lungs is shown at 4 d.p.i. (B). (n = 3 mice per group per time point). Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) For adoptive transfer of serum, Ad5-hAPN- and Ad5-hACE2-transduced IFNAR−/− C57BL/6 mice were intranasally infected with 1.5 × 105 TCID50 of 229E and 1.0 × 104 PFU of NL63 in 75 μL DMEM, respectively. The mouse immune sera were obtained 4 wk postinfection. Then, 150 μL serum was transferred into Ad5-hACE2-transduced mice intravenously (i.v.) 1 d before SARS-CoV-2 infection. Weight changes (n = 5 mice) were monitored daily, and viral titers in lungs were measured at the indicated time points (n = 3 mice per group per time point). (D) The schematic diagrams of T cell depletion from 229E or NL63 infected mice and SARS-CoV-2 challenge. (E) For systemic depletion of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells, mice were infected with 229E (Left) or NL63 (Right). Eighteen days later, mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 0.5-mg anti-CD4 antibody (clone GK1.5) and 0.1-mg anti-CD8 antibody (clone 2.43) 2 d before and on the day of SARS-CoV-2 (beta variant) infection. Virus titers in the lungs were measured at the indicated time points. Titers are expressed as FFU/g tissue (n = 3 or 4 mice per group per time point). (*P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.005, ***P ≤ 0.0005, ****P ≤ 0.0001).