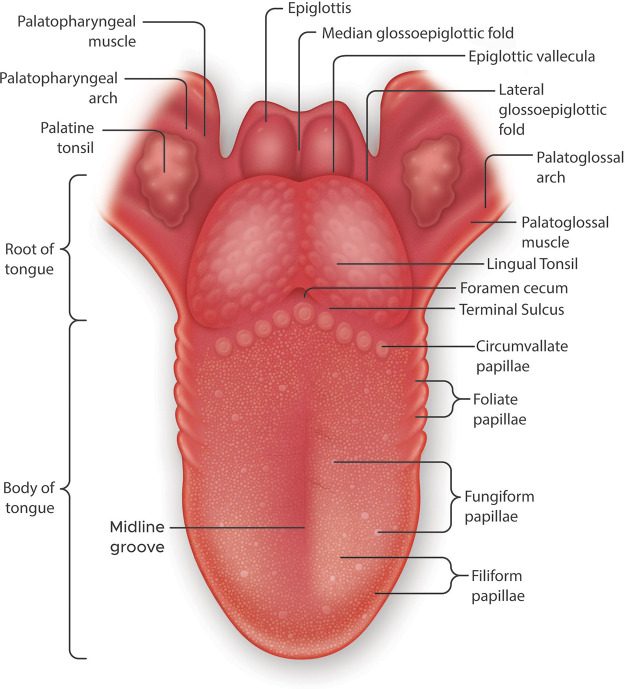
FIGURE 1.
Gross anatomy of the human tongue emphasizing the locations of taste papillae. The tongue is divided transversely into the root or radix lingue (the posterior third) and the body of the tongue or corpus lingue (the anterior two-thirds). The root of the tongue is a papilla-free mucosa, covered with mucous glands and lymphatic tissue, referred to as the lingual tonsil. The 3 types of taste papillae are located in the body of the tongue. Circumvallate papillae are in a V-shaped arrangement at the back of the tongue. The foliate papillae consist of some ridges and slits generally arranged irregularly along the sides of the tongue. The fungiform papillae are the most numerous of the taste papillae and are located on the anterior surface of the tongue interspersed with filiform papillae. Both types of papillae are sparse along the lingual margin and abundant in the middle regions.