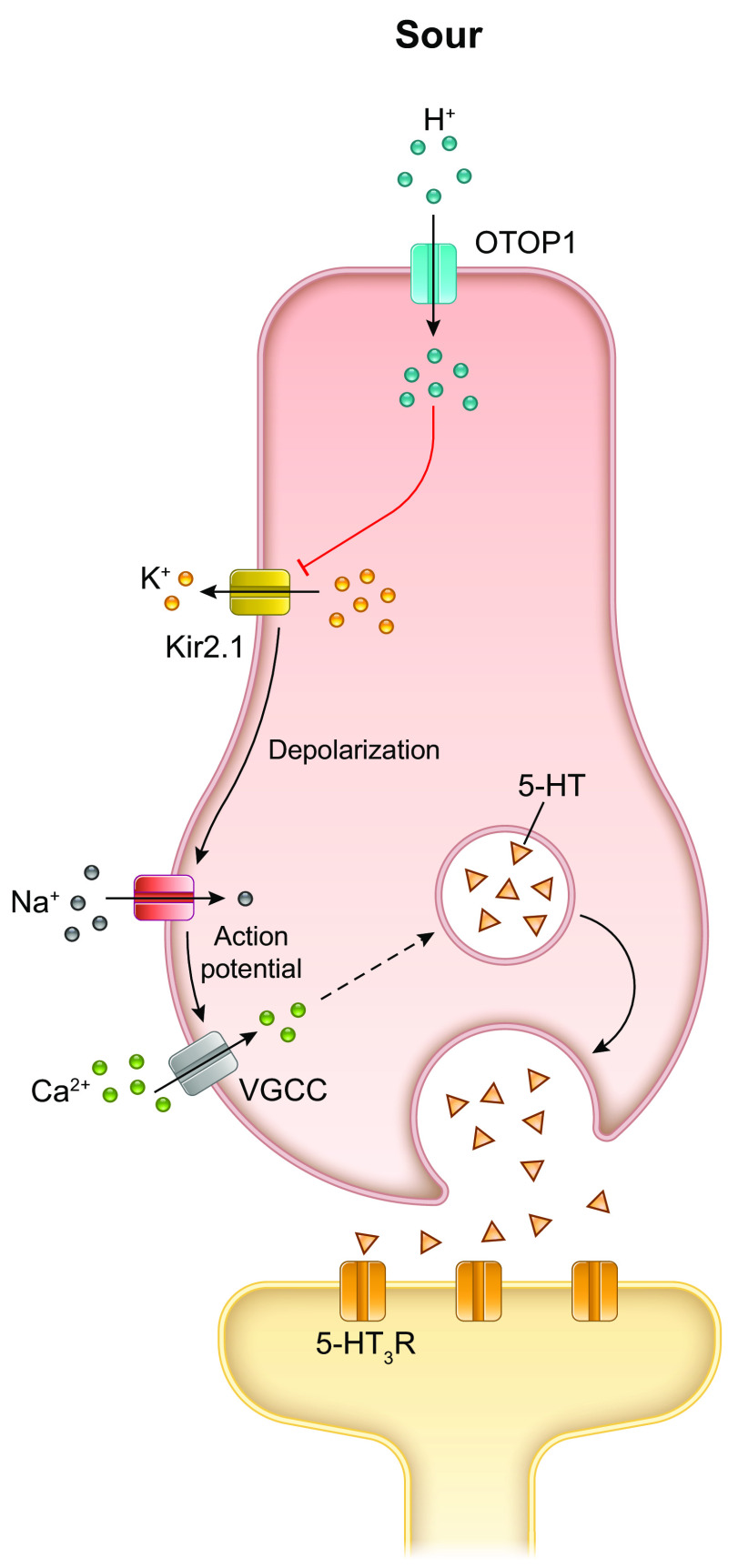
FIGURE 7.
Mechanism of transduction of sour taste. OTOP1 is recognized as the sour receptor and conducts the H+ ions (protons) from acids into the cell cytosol. The influx of cations causes the membrane potential to change direction, and the change in intracellular pH blocks KIR2.1 K+ channels, which further depolarizes the membrane potential. With sufficient depolarization, voltage-gated Na+ channels open causing a train of action potentials that open voltage-gated calcium channels and lead to release of the neurotransmitter 5-HT. 5-HT released at the synapses activates the afferent nerve fibers via excitatory 5-HT3 receptors (R). Image created with BioRender.com, with permission.