Figure 1.
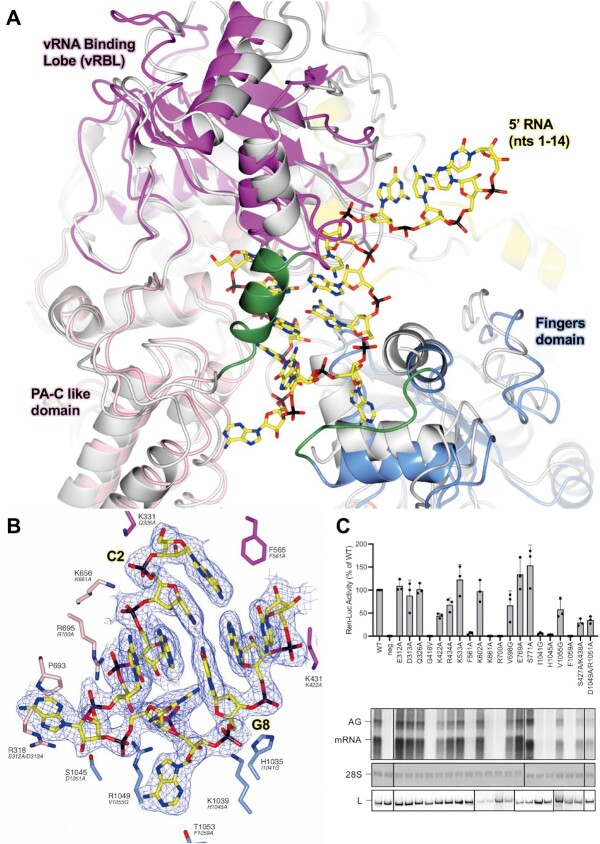
Conformational changes following the binding of the 5′ cRNA hook. (A) The SFTSV L protein (5′ HOOK) is shown with the published apo structure of the SFTSV L protein (PDB: 7ALP, backbone coloured grey) superposed by SSM in CCP4mg (51). A short 3-turn α-helix (M437–H447) and loop (H1038–D1046), which are both stabilized by the binding of the 5′ cRNA nts, are shown in green. (B) A close-up of the SFTSV L protein hook-binding site is shown with the early-elongation map overlaid. Bound 5′ cRNA is shown and coloured yellow with the exception of C2 and G8, which together form the only cognate base-base interaction and are labelled. Residues from the SFTSV L protein are labelled and coloured according to the assigned domain (pink for the PA-C like-domain, blue for the fingers, and magenta for the vRBL) with the corresponding RVFV L protein residue shown in black italicized text underneath. Not all hook-interacting residues are shown for clarity. (C) RVFV mini-replicon data for L protein with mutations in the proposed 5′ hook binding site presenting luciferase reporter activity (in standardized relative light units relative to the wild-type L protein (WT)). Data were presented as mean values ± SD of three biological replicates (n = 3). All biological replicates are shown as black dots (top panel). Middle panels present Northern blotting results with signals for antigenomic viral RNA (AG, equal to cRNA), viral mRNA (mRNA) and 28 S ribosomal RNA (28 S) as a loading control, and the bottom panel shows Western blot detection of FLAG-tagged L proteins (L) to demonstrate general expressibility of the mutants. Uncropped original blots/gels are provided in the Supplementary Data.