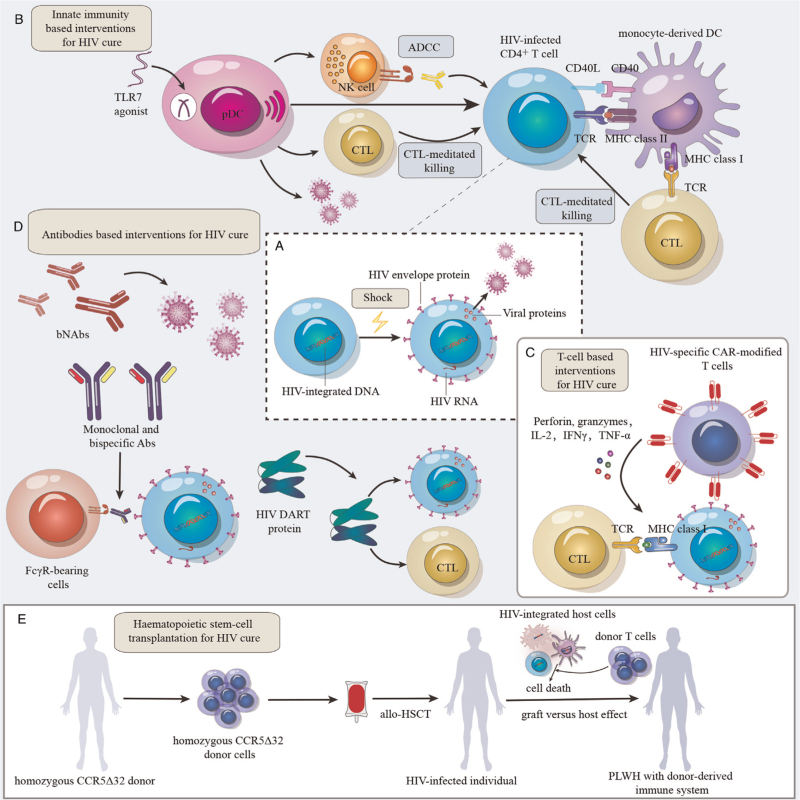
Figure 2.
Immune interventions for HIV cure. (A) “Shock” HIV out of hiding. HIV latency in reservoirs is reversed, leading to increases in viral gene expression and viral protein production. (B) Innate immunity-based interventions for HIV cure. TLR7 agonists and pDCs reactivate HIV-infected cells. HIV-infected cells can be recognized and killed by CTLs and NK cells. MoDC induce CTL and CD4+ T cell responses through Ag presentation. DC-based immunotherapeutic vaccines also involve CD40L, which can enhance DC maturation, interleukin(IL)-12p70 (IL-12p70) production and Ag presentation. (C) T cell-based interventions for HIV cure. CTL-mediated immunotherapy plays a critical role in eliminating the HIV reservoir. CAR-T cells target HIV binding sites on the surface of reactivated reservoir cells and secrete granzymes and cytokines to kill HIV-infected cells. (D) Antibody-based interventions for HIV cure. HIV-specific bNAbs can bind with different epitopes of HIV Env and promote the elimination of HIV reservoirs. Bispecific Abs can simultaneously bind with two different Ag binding sites or epitopes with different inhibitory effects on HIV Env to produce immune responses. DART proteins can improve the recognition of HIV Env on the surface of infected cells and recruit effector cells to eliminate infected cells. (E) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for HIV cure. Allo-HSCT with homozygous CCR5Δ32 donor cells may achieve HIV remission, further supporting the development of functional HIV cures. The graft-versus-host effect may be a key factor in achieving a sterilizing cure of HIV infection after allo-HSCT. Abs: Antibodies; ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity; Ag: Antigen; allo-HSCT: Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; bNAbs: Broadly neutralizing Abs; CAR-T: Chimeric antigen receptor T; CCR5: C-C chemokine receptor 5; CD40: Cluster of differentiation 40; CD40L: CD40 ligand; CTLs: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes; DART: Dual-affinity retargeting; DC: Dendritic cell; DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid; FcγR: Fc gamma receptor; HIV:Human immunodeficiency virus; HIV Env: HIV envelope; IFNγ: Interferon γ; IL-2: Interleukin-2; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; MoDC: Monocyte-derived DCs; NK: Natural killer; pDCs: Plasmacytoid DCs; PLWH: People living with HIV; RNA: Ribonucleic acid; TCR: T-cell receptor; TLR7: Toll-like receptor 7; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.