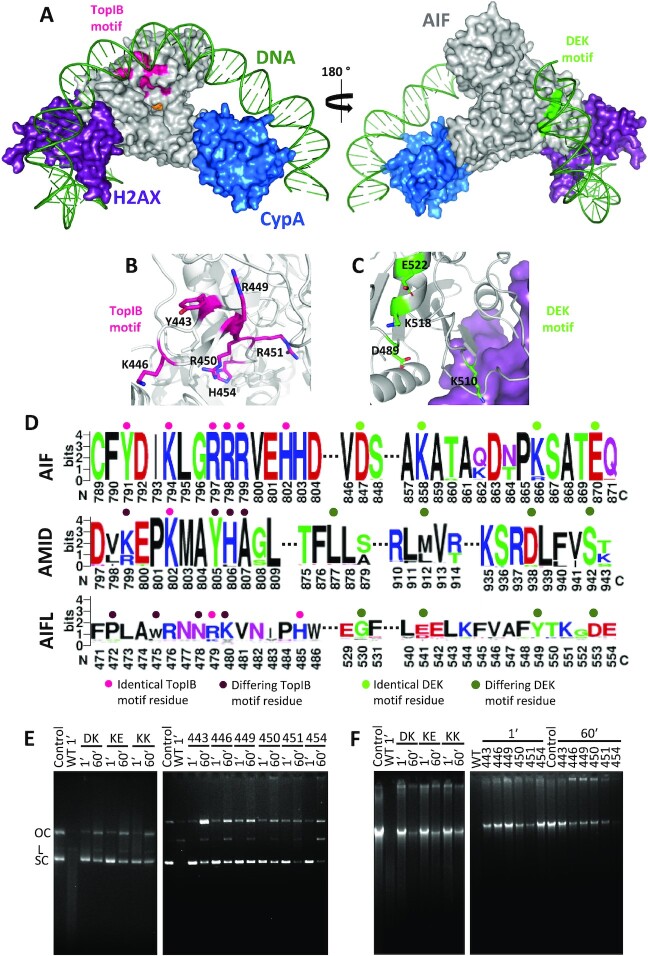
Fig. 4.
Potential nuclease domains in AIF and effect of TopIB and DEK mutations on its nuclease activity. (A) Model for the binding of dsDNA (green) to the energetically optimized degradosome assembly (color codes for proteins as in Figure 1F). The potential nuclease TopIB and DEK motifs appear colored in magenta and green respectively on the AIF surface. Environment of (B) TopIB and (C) DEK motifs highlighting relevant residues as sticks. (D) Sequence logo (https://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi) for the conservation of identified TopIB and DEK motifs in human AIF in sequences of AIF family members (AIF, AIFL, and AMID) from different organisms. Key residues identical to those in human AIF TopIB and DEK motifs are marked respectively with a pink or green dot on top, while differing residues are marked with darker tones. While the motifs are significantly conserved within the AIF subfamily members, they do not extend to either AMID or AIFL proteins. AIF motifs, Yx2Kx2RRRx2H and Dx9Kx7Kx3E. AMID equivalents, kx2Kx2yha and lx33mx23dx3s. AIFL equivalents, px2wx2nRkx4H and gx10ex7yx3d. Capital letters indicate residues conserved across the different members, lower case letters stand for those not conserved. Further details in the Supplementary Material. Nuclease activity of different AIFΔ101 TopIB and DEK variants (E) on a double-stranded supercoiled pET-28a(+) plasmid (250 ng) and (F) on human genomic DNA (500 ng). dsDNA substrates were respectively mixed with the AIFΔ101 variants (250 ng) in 20 mM Tris/HCl, pH 8.0, 0.1 mM CaCl2 and 1 mM MgCl2. Samples were incubated for 1 and 60 min at 37°C. Control, stands for plasmid or genomic DNA substrate alone. OC, L, and SC stand, for open circular, linear, and supercoiled, respectively. Code for mutated residues in AIFΔ101 variants: 443, Y443A; 446, K446A; 449, R449A; 450, R450A; 451, R451A; 454, H454S; DK, D489A/K518A; KE, K518A/E522A; and KK, K510A/K518A.