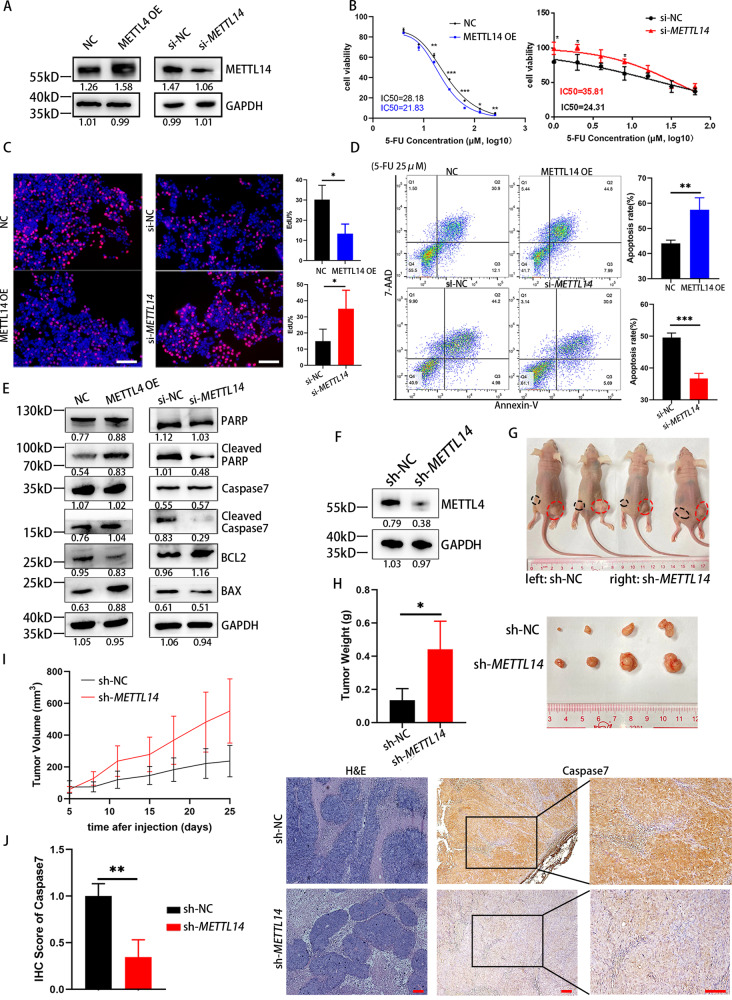
Fig. 3. METTL14 promotes the 5-FU-induced apoptosis.
A Overexpression and knockdown efficiency of METTL14 in HCT116 cells. B The 5-FU IC50 of HCT116 cells in different groups. C EdU proliferation assay of HCT116 cells with different METTL14 expression levels after 5-FU treatment. P (NC vs. METTL14 OE) = 0.0265; P (si-NC vs. si-METTL14) = 0.0379. D Annexin V-PE/7AAD apoptosis assay of HCT116 cells with different METTL14 expression levels after 5-FU treatment. P (NC vs. METTL14 OE) = 0.0095; P (si-NC vs. si-METTL14) = 0.0005. E Western blot analysis of PARP, Cleaved PARP, Caspase7, Cleaved Caspase7, BCL2 and BAX protein expression levels in different METTL14 expression levels HCT116 cells treated with 5-FU. F Knockdown efficiency of stably transfected METTL14 CRC cells. G Nude mice were implanted with tumor cells subcutaneously. H Tumor sizes and weights of xenograft after 6 times 5-FU treatment. P = 0.0360. I The changes of tumors volume during the treatment of 5-FU. J H&E and immunohistochemistry analysis of Caspase7 levels in two groups. P = 0.0077. Results shown were representative of at least 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance in (B-D), (H), (J) was assessed by student’s t-test. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. Error bars, SD. Scale bars, 400 μm in (C), 100 μm in (J). The IHC score and grey value of protein bands has been quantified by Image J.