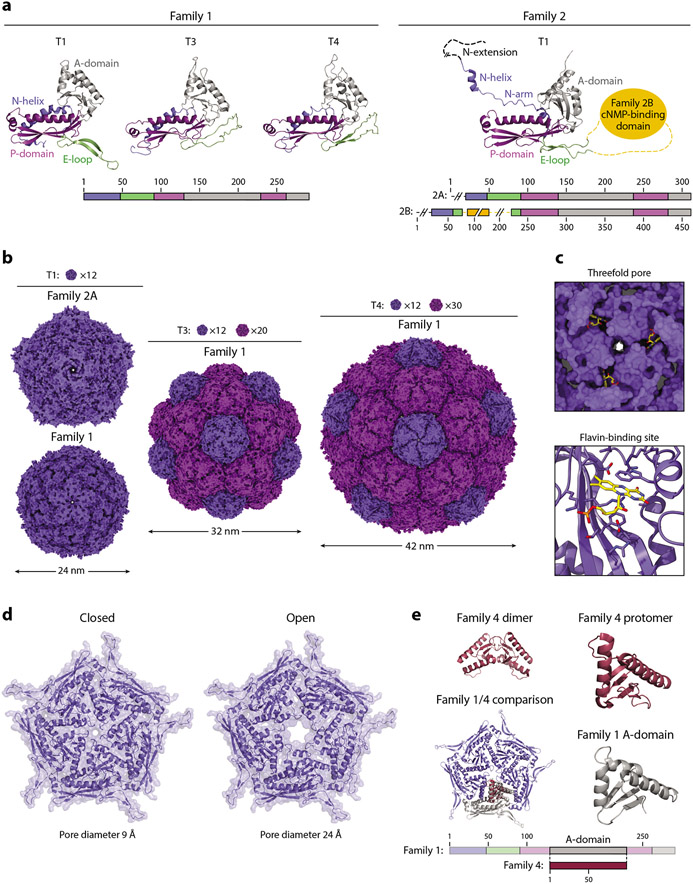
Figure 4.
Structure and function of the encapsulin shell. (a, left) Family 1 and (right) Family 2 encapsulin protomers colored by their conserved HK97-fold domains. Protomers of Family 1 T1 (3DKT), T3 (4PT2), and T4 (6NJ8), and Family 2 T1 (6X8M) shells are shown. (b) Exterior view down the fivefold symmetry axis of T1, T3, and T4 shells. Pentameric and hexameric facets are colored dark and light purple, respectively. The number of facets needed to tile a closed shell of a given triangulation number is shown. The same structures were used as in panel a. (c) Flavin-binding site in the Thermotoga maritima T1 shell (7KQ5). (Top) View down the threefold axis and (bottom) a zoomed-in view of the binding site. Residues within 5 Å of the flavin moiety are shown as sticks. (d) The closed and open states of the pentameric pores of the Haliangium ochraceum T1 shell are shown. (e) Comparison of a Family 4 encapsulin (2PK8) with a Family 1 pentameric facet (3DKT). Abbreviations: A-domain, axial domain; cNMP, cyclic nucleotide; E-loop, extended loop; N-helix, N-terminal helix; P-domain, peripheral domain.