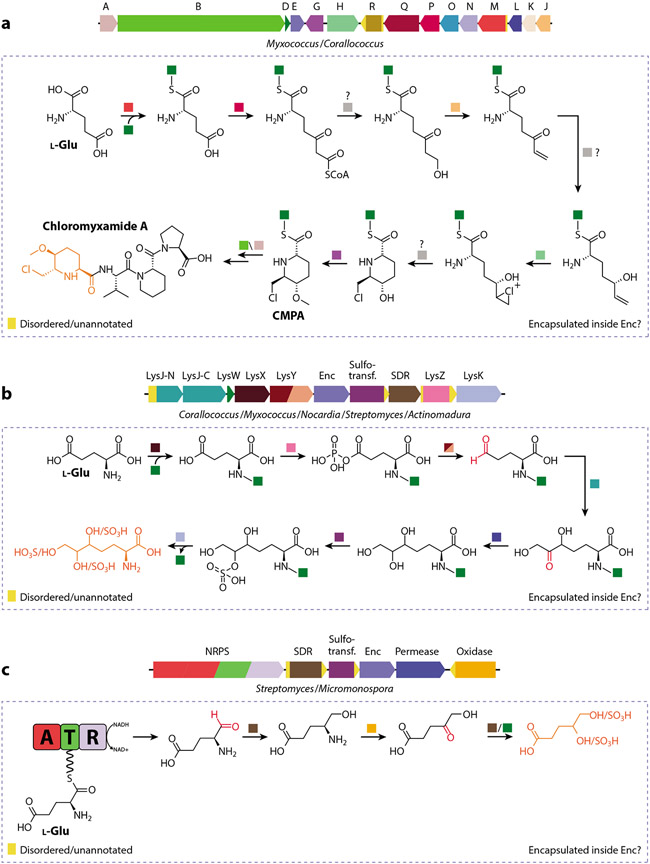
Figure 6.
Select Family 3 encapsulin operons and proposed biosynthetic pathways. (a) Chloromyxamide biosynthetic gene cluster and its proposed AmCP-dependent biosynthesis. Some of the depicted reactions may happen inside a Family 3 encapsulin, indicated by the dotted box. The chemical logic behind encapsulation may be the sequestration of reactive or toxic aldehyde/ketone or chlorination intermediates. The chlorinated CMPA building block is highlighted (orange). Question marks indicate uncertainty about steps as depicted. Abbreviations: A, ornithine cyclodeaminase; B, hybrid nonribosomal peptide synthetase/type I polyketide synthase; CMPA, 6-chloromethyl-5-methoxypipecolic acid; D, LysW; E, Enc, Family 3 encapsulin; G, SAM-dependent methyltransferase; H, rubber oxygenase A; J, enoyl-CoA hydratase; K, TetR/AcrR family transcriptional regulator; L, NADP-dependent oxidoreductase; M, AMP-dependent synthetase; N, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; O, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; P, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase; Q, acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; R, aldehyde dehydrogenase. (b) Uncharacterized Family 3 gene cluster and proposed AmCP-dependent biosynthesis. Potentially reactive carbonyl intermediates are shown in red, while a putative product is shown in orange. Abbreviations: AmCP, amino group carrier protein; Enc, Family 3 encapsulin; LysJ-N/C, transketolase; LysK, AmCP-amino acid carboxypeptidase; LysW, AmCP; LysY, AmCP–amino acid phosphate reductase; LysX, amino acid–AmCP ligase; LysZ, AmCP–amino acid kinase; SDR, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase; Sulfotrans., sulfotransferase. (c) Family 3 encapsulin embedded in an uncharacterized NRPS-dependent biosynthetic gene cluster. Potentially reactive carbonyl intermediates are shown in red, and a putative product is shown in orange. Abbreviations: A, adenylation domain; AmCP, amino group carrier protein; CMPA, 6-chloromethyl-5-methoxypipecolic acid; Enc, Family 3 encapsulin; NRPS, nonribosomal peptide synthetase; R, reduction domain; SDR, short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase; Sulfotrans., sulfotransferase; T, thiolation domain.