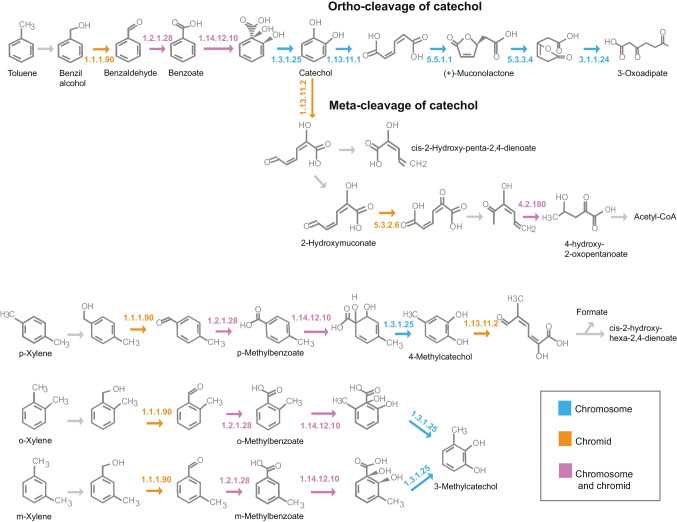
Fig. 8.
Pathways associated with the degradation of aromatic compounds, obtained with the KEGG Mapper tool, indicating genes detected in the chromosome (in blue), the chromid (in orange), or in both replicons (in pink) of strain GeG2T genome. 1.1.1.90: aryl-alcohol dehydrogenase; 1.2.1.28: benzaldehyde dehydrogenase (xylC); 1.14.12.10: benzoate/toluate 1,2-dioxygenase subunit alpha (benA-xylX); 1.3.1.25: dihydroxycyclohexadiene carboxylate dehydrogenase (benD-xylL); 1.13.11.1: catechol 1,2-dioxygenase (catA); 5.5.1.1: muconate cycloisomerase (catB); 5.3.3.4: muconolactone D-isomerase (catC); 3.1.1.24: 3-oxoadipate enol-lactonase (pcaD); 1.13.11.2: catechol 2,3-dioxygenase (dmpB-xylE); 5.3.2.6: 4-oxalocrotonate tautomerase (praC-xylH); 4.2.1.80: 2-keto-4-pentenoate hydratase (mhpD)