Figure 4. Sural Nerve Biopsy Specimens From Patients With Anti-MAG Neuropathy.
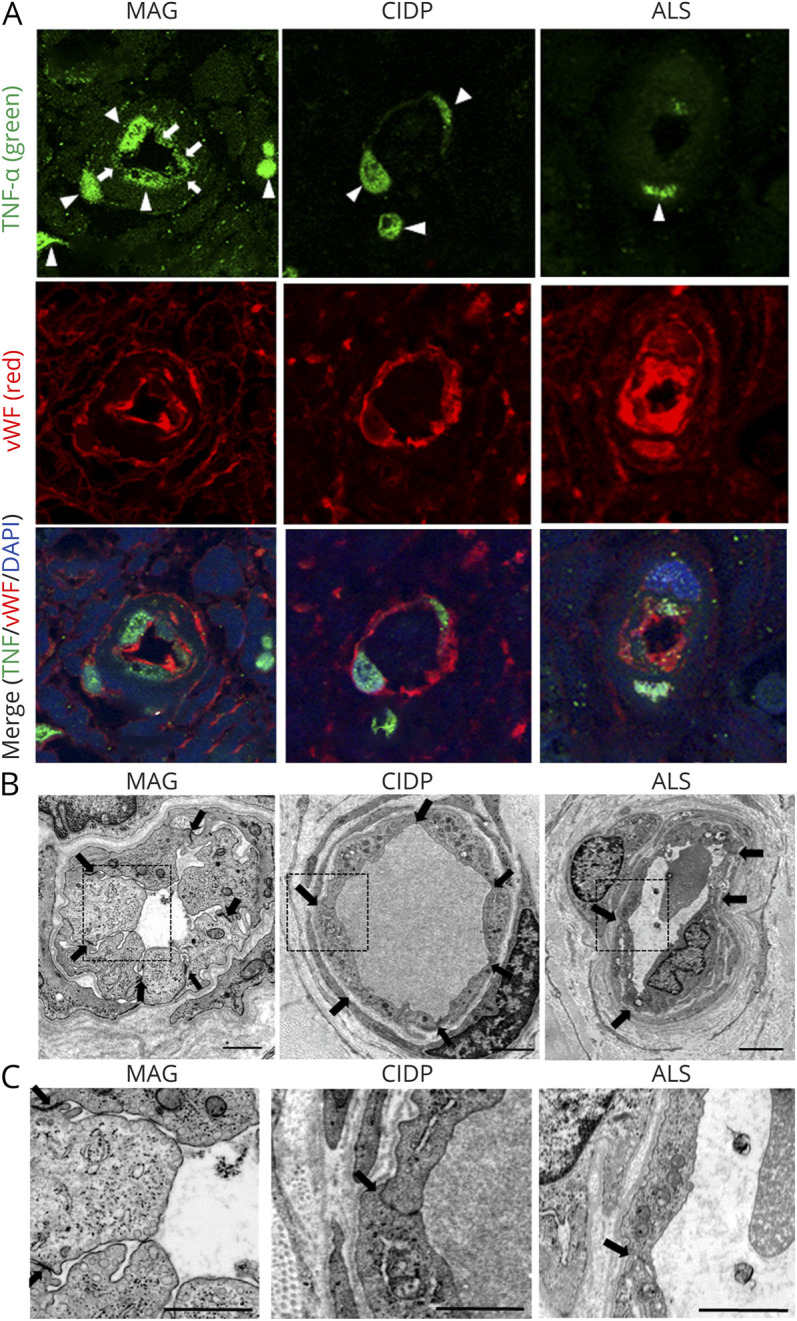
Sural nerve biopsy specimens obtained from 4 patients with MAG IgM neuropathy, 2 patients with ALS as noninflammatory control samples and 1 patient with CIDP as inflammatory control were analyzed. (A) TNF-α immunostaining showed the expression of TNF-α in BNB endothelial cells of biopsy specimens from patients with anti-MAG neuropathy (arrows), but not those from noninflammatory or inflammatory controls. Nuclear staining of TNF-α observed in all samples of MAG neuropathy, CIDP, and ALS was nonspecific (arrowheads). Upper panel: TNF-α (green); middle panel: Von Willebrand Factor (vWF) (red), an endothelial cell marker; lower panel: merge TNF-α (green)/vWF (red)/DAPI (blue). (B and C) Electronic microscopy showed the hypertrophy of endothelial cells and the preservation of the tight junctions between adjacent endothelial cells of BNB endoneurial vessels in biopsy specimens from patients with anti-MAG neuropathy (B) and more abundant vesicles in BNB endothelial cells in biopsy specimens from patients with anti-MAG neuropathy, in comparison to those from patients with ALS and CIDP (C). Scale bar, 1 μm. ALS = amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; BNB = blood-nerve barrier; CIDP = chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy; IgM-MG = IgM–monoclonal gammopathy neuropathy; MAG = myelin-associated glycoprotein; TNF = tumor necrosis factor.
