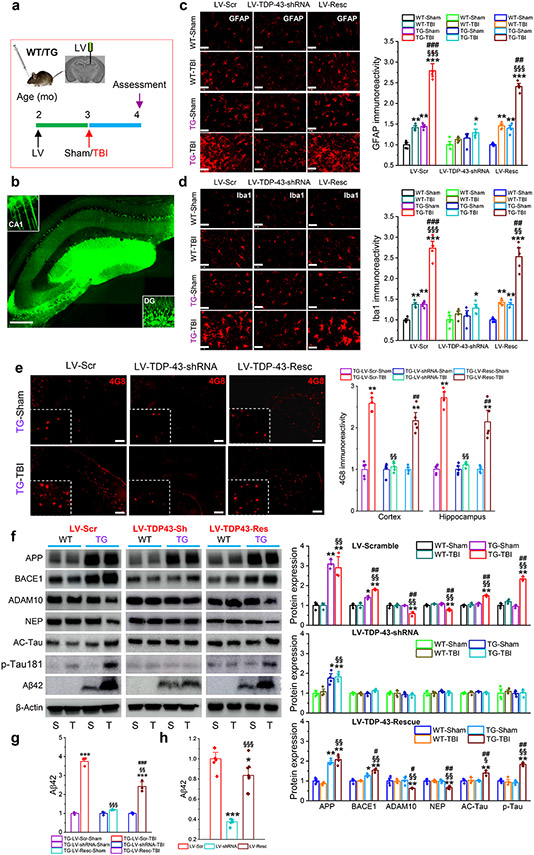
Figure 2.
Silencing of TDP-43 alleviates single mild CHI-exacerbated neuropathology in APP TG mice. a, Schematic illustration of the experimental protocol. WT and APP TG mice at two months of age were stereotaxically injected with LV 30 days prior to a single mild CHI, and all the assessments were performed 30 days after a single mild CHI. b, A representative image showing expression of GFP in the hippocampus injected with LV. Scale bar: 200 μm. c, Immunoreactivity of GFAP (astrocytic marker) in the ipsilateral hippocampus of WT and APP TG mice that received LV expressing scramble control, TDP-43-shRNA, or shRNA-resistant TDP-43. The data are means ±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with WT-Sham; §§§P<0.001 compared with WT-TBI; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 compared with TG-Sham (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). Scale bars: 40 μm. d, Immunoreactivity of Iba1 (microglial marker) in the ipsilateral hippocampus of WT and APP TG mice that received LV expressing scramble control, TDP-43-shRNA, or shRNA-resistant TDP-43. The data are means ±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with WT-Sham; §§P<0.01, §§§P<0.001 compared with WT-TBI; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 compared with TG-Sham (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). Scale bars: 40 μm. e, Single mild CHI-aggravated formation of Aβ plaques is prevented by knockdown of TDP-43 in APP TG mice. The data are means ±SEM. **P<0.01 compared with TG-LV-Scr-Sham; §§P<0.01 compared with TG-LV-Scr-TBI; ##P<0.01 TG-LV-Resc-Sham (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). f, Immunoblot analysis of hippocampal protein expressions in WT and APP TG mice that were injected with LV expressing scramble control, TDP-43-shRNA or shRNA-resistant TDP-43 prior to receive a single mild CHI. The data are means ±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 compared with WT-Sham; §P<0.05, §§P<0.001 compared with WT-TBI; #P<0.05, ##P<0.001 compared with TG-Sham (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=3~4 animals/group). g, Quantification of Aβ42 displayed in f as it is not detectable in WT animals. The data are means ±SEM. ***P<0.001 compared with TG-LV-Scr-Sham; §§P<0.01, §§§P<0.001 TG-LV-Scr-TBI; ###P<0.01 TG-LV-Resc-Sham (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=3~4 animals/group). h, ELISA analysis of hippocampal Aβ42 in APP TG mice treated with LV expressing scramble control, TDP-43-shRNA, or shRNA-resistant TDP-43. The data are means ±SEM. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 compared with LV-Scr, §§§P<0.001 LV-shRNA (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=6~8 animals/group).