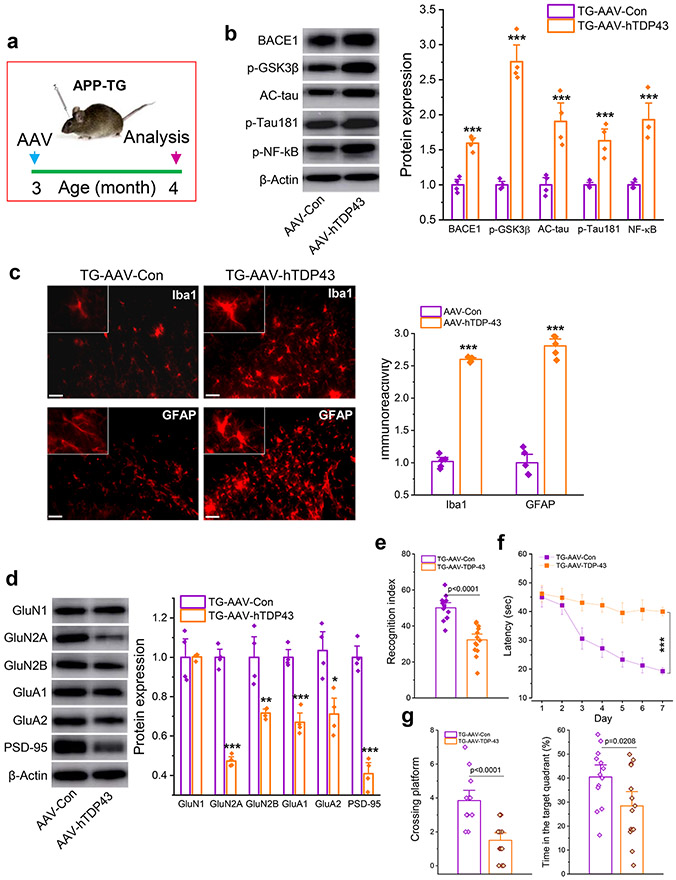
Figure 8.
Overexpression of TDP-43 aggravates neuropathology and accelerates impairments of learning and memory in APP TG mice. a, Schematic illustration of the protocol for injection of AAV vectors. AAV9-CMV-hTDP-43.eGFP vectors or AAV9-CMV-eGFP control vectors were stereotaxically injected into the hippocampus of APP TG mice at three months of age and all the assessments were made 30 days after injection of AAV vectors. b, Immunoblot analysis of BACE1, p-GSK3β, AC-tau, p-tau181, and p-NF-kB. ***P<0.001 compared with TG-AAV-Con (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=4 animals/group). c, Immunoreactivity of microglia and astrocytes in the hippocampus of APP TG mice. ***P<0.001 compared with TG-AAV-Con (ANOVA with Bonferroni post post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). d, Immunoblot analysis of glutamate receptor subunits and PSD-95 in the hippocampus of APP TG mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with TG-AAV-Con (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=4 animals/group). e, NOR test in APP TG mice that received AAV-hTDP43. (ANOVA with Bonferroni post post-hoc test, n=13~14 animals/group). f, Learning acquisition in the MWM test. ***P<0.001 compared with TG-AAV-Con (ANOVA with repeated measures). g, The probe test that was performed 24 hrs following 7-day invisible training. (ANOVA with Bonferroni post post-hoc test, n=13~14 animals/group).