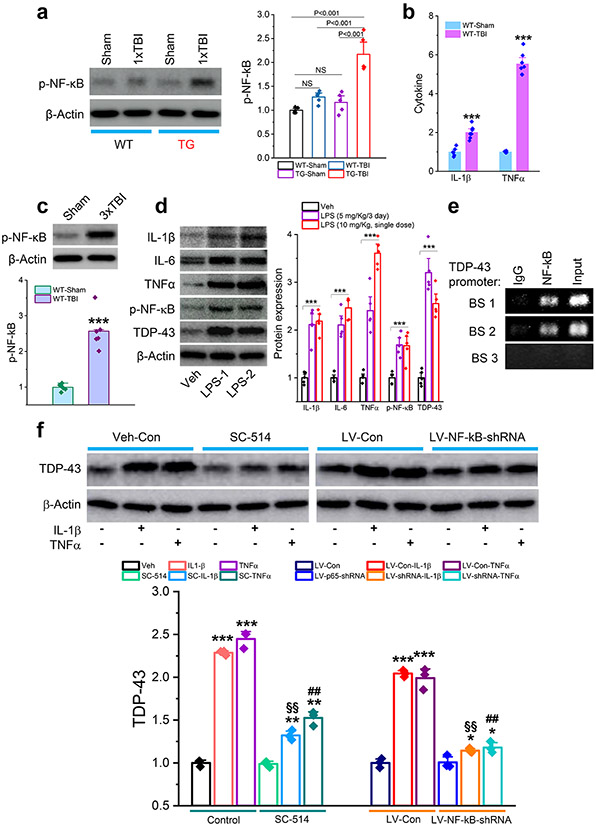
Figure 9.
Neuroinflammation causes aberrant production of TDP-43 via NF-κB signaling. a, Expression of phosphorylated NF-κB (p-NF-κB) in the hippocampus of APP TG and WT mice that received a single mild CHI. The analysis was performed 30 days after the impact. The data are means ±SEM (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). b, Cytokine formation in the hippocampus of WT mice that received repeated mild CHI. ELISA analysis IL-1β and TNFα was conducted 24 hours following the last impact. The data are means ±SEM. ***P<0.001 (ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test, n=6~7 animals/group). c, Expression of p-NF-κB in the hippocampus of WT mice that received three mild CHI. The analysis was performed 30 days after repeated mild CHI. The data are means ±SEM (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=6 animals/group). d, Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) increases expression of cytokines, p-NF-κB, and TDP-43 in the hippocampus of WT mice. LPS was injected (i.p.) with repeated doses at 5 mg/kg (Once a day for three days, LPS-1) or a single dose at 10 mg/kg (LPS-2). Immunoblot analysis was performed 24 hours after injection. The data are means ±SEM. ***P<0.001 compared with the vehicle control (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD post-hoc test, n=5 animals/group). e, Chromatin immunoprecipitation (CHIP) analysis of NF-κB p65 binding activity at the promoter of the TDP-43 gene. f, Proinflammatory cytokine-increased expression of TDP-43 is attenuated by pharmacological or genetic inhibition of NF-κB p65. Hippocampal neurons in cultures from control mice were treated with SC-541 (IKKβ inhibitor, 100 μM) or transfected with LV expressing NF-κB p65-shRNA for three days. IL-1β or TNFα (10 ng/ml)-induced expression of TDP-43 was assessed 24 hours after treatment with cytokines. The data are means ±SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with the vehicle control or LV-Con; §§P<0.01 compared with IL-1β; ##P<0.01 compared with TNFα (ANOVA with Fisher's PLSD test post-hoc test, n=3).