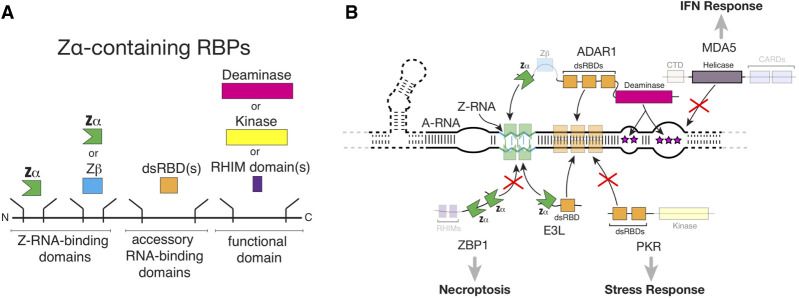
FIGURE 3.
Competition for Z-RNA by dsRNA sensors modulates the innate immune response. (A) General domain architecture of Zα-containing RBPs, all of which have one or more Zα domains on their amino terminus, followed by one or more dsRBDs, and finally by a functional domain (such as a deaminase or kinase domain). (B) Summary of our current understanding of the interactions between Zα-containing proteins and Z-RNA within a hypothetical folded molecule, and how these interactions modulate pathways that depend on dsRNA sensor activation. Direct shielding of dsRNA and Z-RNA by viral E3L as well as host ADAR1 proteins prevent recognition by ZBP1 and PKR, preventing activation of necroptosis and the stress response. In addition, editing of dsRNA by ADAR1 prevents MDA5 activation. Abbreviations are explained within the text, except for CARDs (caspase recruitment domains), which mediate interactions with downstream signaling proteins, and RHIM (receptor-interaction protein [RIP] homotypic interaction motifs).