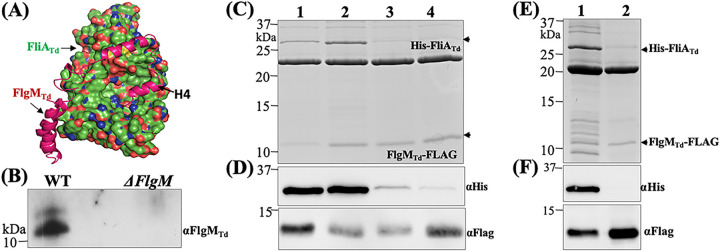
FIG 4.
FliATd interacts with FlgMTd. (A) Protein-protein docking analysis of FliATd and FlgMTd. The homology models of FliATd and FlgMTd were first generated using the cocrystal structure of A. aeolicus s28/FlgM complex (PDB code 1rp3), and then protein-protein docking analysis was conducted on the ClusPro server, with FliATd shown as a molecular surface and FlgMTd shown as a backbone ribbon. (B) Coimmunoprecipitation (co-IP). This assay was performed using T. denticola whole-cell lysates and a polyclonal antibody against FliATd (αFliATd). The final co-IP eluates were probed using anti-FlgMTd. A deletion mutant of flgMTd (ΔflgM) was used as a negative control. (C to F) Copurification of N-terminal His-tagged FliATd (His-FliATd) and C-terminal FLAG-tagged FlgMTd (FlgMTd-FLAG). The two tagged proteins and their corresponding site-directed mutated or truncated proteins were coexpressed in the E. coli BL21 Star(DE3) strain and then purified using FLAG beads. The resulting samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE (C and E), followed by immunoblotting analysis (D and F) using either anti-FLAG (αFlag) or anti-His (αHis) antibodies. In panels C and D, in addition to the wild-type FliATd protein (lane 1), three site-directed mutated recombinant proteins were included: E221D (lane 2), V231E (lane 3), and a double mutation of E221D andV231E (lane 4). In panels E and F, lane 1 shows the wild-type FlgMTd protein and lane 2 shows a truncated FlgMTd protein without the H4′ helix (79 to 93 aa).