FIG 5.
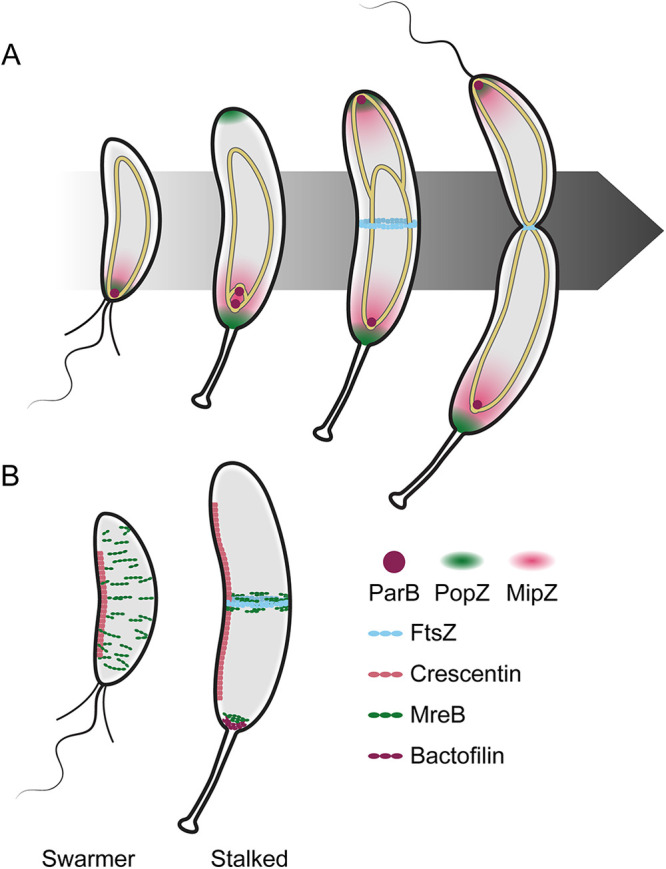
Spatial regulation of morphogenesis in Caulobacter. (A) FtsZ localization is driven by interactions with the chromosome (gold-outlined ellipse). ParB (plum circle) binds the parS sequence near the origin (circles at the ends of the chromosomes) and associates with PopZ (green cloud) at the pole. ParB translocates with the newly synthesized origin and anchors it to the nascent swarmer pole (top of cells). MipZ (pink cloud) binds to ParB and to the DNA to form a gradient, limiting FtsZ (cyan) polymerization to midcell in stalked and predivisional cells. (B) Localization of four major cytoskeletal proteins (crescentin, pink; MreB, green; FtsZ, cyan; bactofilin, plum) shown in swarmer (left) and stalked (right) cells. Crescentin directs curvature in both cell types. MreB directs elongasome localization and global cell wall insertion in swarmer cells and midcell insertion in stalked cells to facilitate elongation. FtsZ directs divisome assembly and cell wall remodeling at midcell in stalked cells to facilitate constriction. Bactofilins and MreB recruit and regulate stalk elongation machinery during the swarmer-to-stalk transition and remain localized at the base of the stalk in stalked cells.
