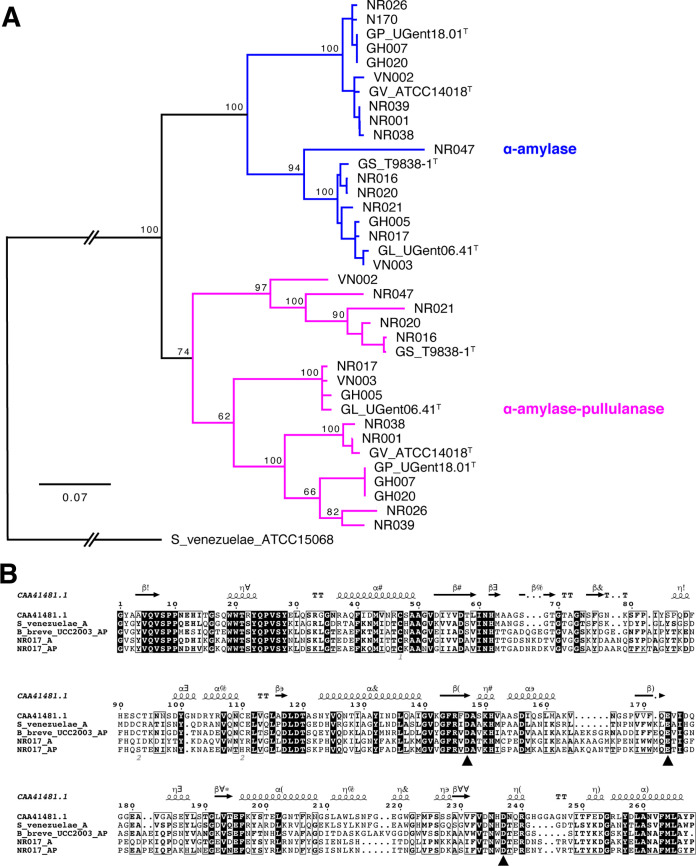
FIG 4.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of all α-amylase domains from 15 Gardnerella isolates and 4 reference strains (indicated with T after the strain name). The tree is rooted with Streptomyces venezuelae ATCC 15068. Trees are consensus trees of 100 bootstrap iterations and constructed using the neighbor-joining method using the Tamura-Nei distance model. The number at major branch points represents the percentage of bootstrap support. (B) Sequence alignment of GH13_32 catalytic domains of G. leopoldii NR017 α-amylase (NR017_A) and α-amylase-pullulanase (NR017_AP) with other functionally characterized GH13_32 members (α-amylases from Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis A23 [GenPept accession number CAA41481] and S. venezuelae ATCC 15068 and amylopullulanase from Bifidobacterium breve UCC2003). Black triangles indicate conserved catalytic residues.