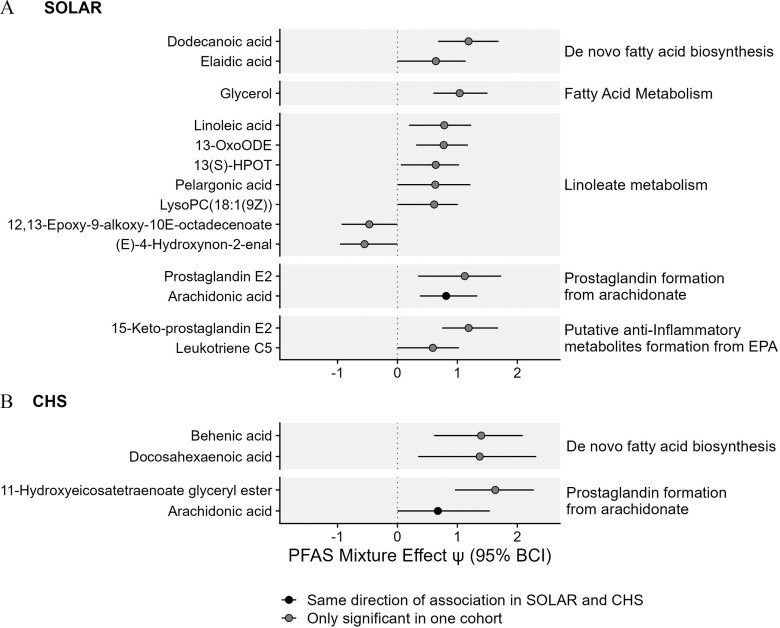
Figure 3.
Associations between PFAS mixtures and metabolites associated with lipid metabolism in (A) adolescents from the SOLAR cohort () and (B) young adults from the CHS cohort (). Effect estimates for PFAS mixture () and the 95% Bayesian credible interval (BCI) estimate the change in metabolite levels (SD of the log-transformed feature intensity) when increasing all PFAS in the mixture from the 30th percentile to the 70th percentile. This estimate is also equivalent to a standardized mean difference calculated between a hypothetical group of individuals with all PFAS at the th percentile vs. a hypothetical group of individuals with all PFAS at the th percentile. Corresponding -values and -values are presented in Table S4. Note: CHS, Children’s Health Study; EPA, eicosapentaenoic acid; HPOT, hydroperoxyoctadecatrienoic acid; LysoPC, lysophosphatidylcholines; OxoODE, Octadecanienoic acid; PFAS, per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances; SD, standard deviation; SOLAR, Study of Latino Adolescents at Risk.