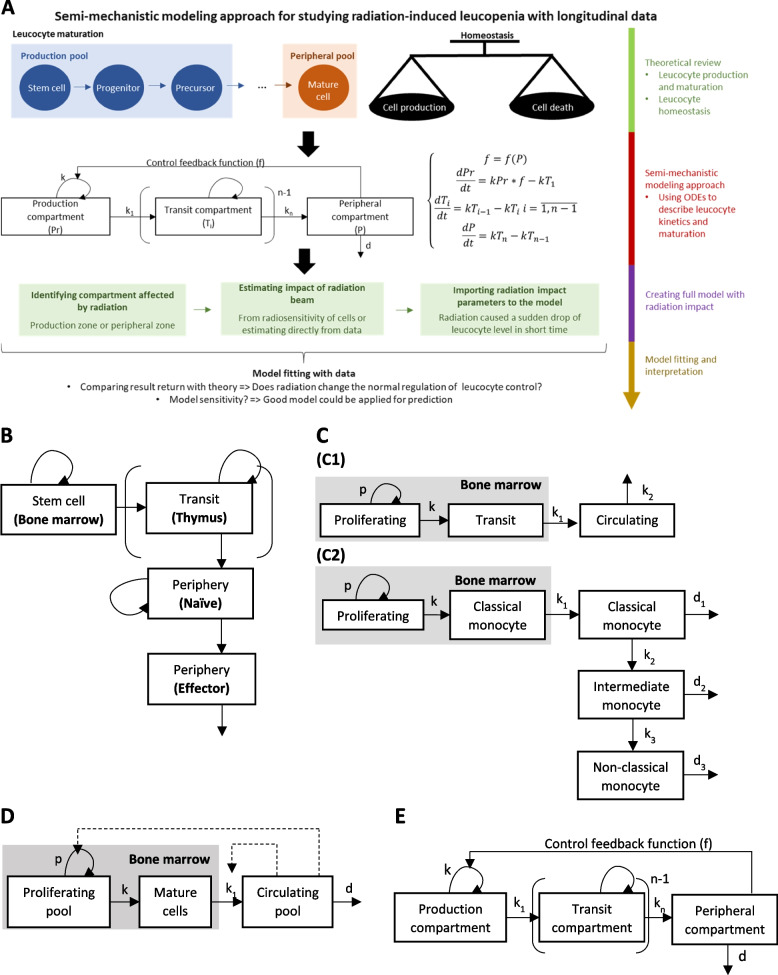
Fig. 7.
A A semi-mechanistic modeling approach framework for investigating radiation-induced leucopenia with longitudinal data. Legend: A model structure (graph and ODE) for cell kinetics was built based on theory of cell production, maturation, and homeostasis. Based on the cell kinetics model, target compartments and parameters of radiation beams must be defined (based on theory and treatment planning system). B Structural model of lymphocyte population kinetics. Legend: This model includes: 1) a stem cell compartment with proliferation (here the bone marrow) and output, yet no input; 2) the thymus in cases of T-cells, with input, proliferation, and output of cells; 3) the peripheral pool of immunocompetent mature T and B lymphocytes, which are divided in transit compartments; 4) an effector compartment formed by antibody-producing plasma cells, which constitutes a simple transit compartment, with input and output (cell loss), yet no proliferation. C Structural model of myeloid population kinetics: (C1) structural model of neutrophil population kinetics. The model considers mitotic neutrophil precursors as a single proliferating pool. Cells in this pool proliferate at a mean rate p. After the last mitosis, the cells enter the transit pool at a rate k. Transit neutrophils remain for a period in the bone marrow before being released into the circulating pool at rate k1. The cells either leave this pool in the direction of other marginal organs or die by apoptosis at rate k2. (C2) Structural model of monocyte population kinetics. The model depicts monocytes in the bone marrow, where their precursors proliferate at rate p and mature at rate k. Mature monocytes are released from the bone marrow at rate k1 into the circulation. In blood, monocytes either mature into intermediate monocytes at rate k2 or disappear from the blood (by death or by moving to other organs) at rate d1. Intermediate monocytes either differentiate into long-lived non-classical monocytes at rate k3 or disappear from the blood at rate d2. Non-classical monocytes are the final differentiation stage, which disappear from the blood at rate d3. D Simplified structural model of myeloid cell population kinetics following cell depletion. This model comprises a proliferating pool, mature pool in bone marrow, and circulating pool. A negative feedback loop was added, in which the proliferating rate and transfer rate from bone marrow to blood were negatively controlled by the circulating pool size. E Compartment description of Friberg’s model. The model consists of a proliferating compartment that is sensitive to drugs, in addition to three transit compartments that represent maturation, and a compartment of circulating blood cells