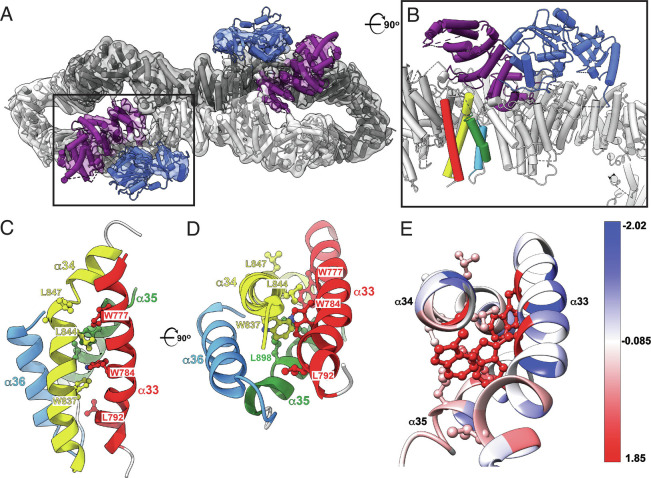
Fig. 3.
Cryo-EM structure of the intact short isoform of human neurofibromin. (A) Top view of the final model of NF1 dimer (cartoon) and the corresponding 3D cryo-EM density (transparent grey surface) showing NF1 protomers in dark and light gray, GRD in purple, and Sec-PH (pleckstrin homology) domain in blue. Boxed area indicates the location of the GRD (purple) and Sec-PH (blue) domains in one of the NF1 protomers. PDB: 8E20, EMDB: EMD-27826. (B) A close-up and rotated view of the boxed area from A shows that helices α33 to α36 (red, yellow, green, and light blue) are located directly below the GRD domain (purple). The view is rotated ~90° clockwise around the horizontal axis when compared to A. (C) Side view of the α33 to α36 helical bundle (ribbon cartoon colored red, yellow, green, and light blue). Severe phenotype mutations map to the region encompassing residues 844 to 847 (side chains shown in ball-and-stick representation). (D) Top view of the same bundle. For clarity, helix α33 is not shown. The view is rotated ~90° clockwise around the horizontal axis relative to C. (E) Residues affected by pathogenic mutations are colored using Kyte-Doolittle amino acid hydrophobicity scale where hydrophobic and polar residues are red and blue, respectively.