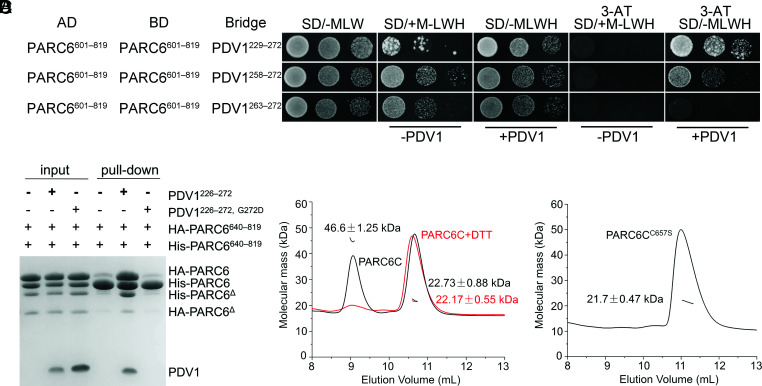
Fig. 6.
Dimerization of PARC6 is regulated by PDV1 and the redox status. (A) Y3H analysis shows that PDV1 promotes the self-interaction of PARC6. Various lengths of the C-terminal domain of PDV1 were tested. Methionine (M) suppresses the expression and accumulation of the bridge protein PDV1. 3-AT is an inhibitor of the enzyme encoded by the reporter gene HIS3. The negative controls are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S13. (B) A pull-down assay shows that the interaction between PDV1 and PARC6 promotes the self-interaction of PARC6. The reaction buffer contains DTT (5 mM), which can reduce disulfide bonds and open the “lid”. Δ, a minor degradation product of the protein. (C) SLS analysis of PARC6C (residues 640 to 819) with or without 5 mM DTT. (D) SLS analysis of PARC6CC657S (residues 640 to 819) indicates that it is a monomer.