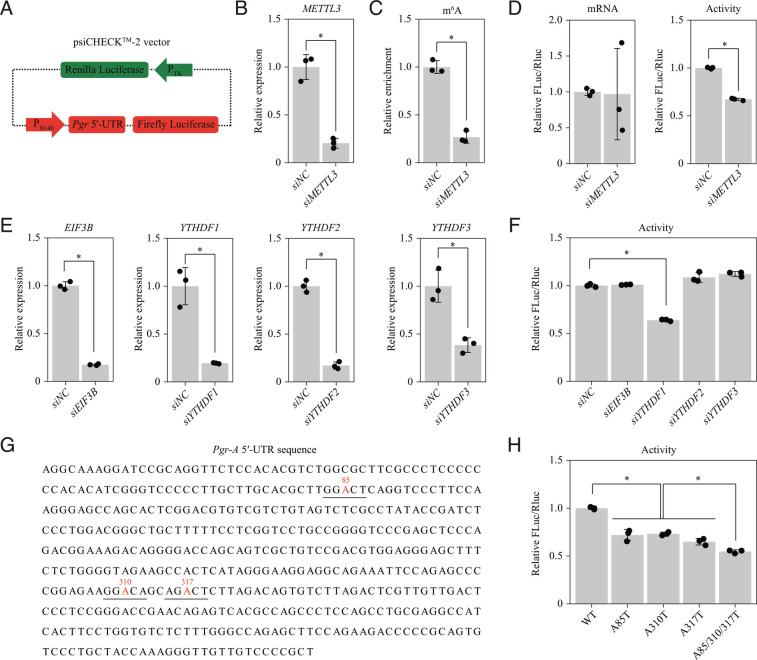
Fig. 6.
M6A modification in the 5′-UTR of Pgr mRNA enhances PGR protein translation efficiency in a YTHDF1-dependent manner. (A–D) Dissecting the role of the Pgr-A 5′-UTR in translation by dual-luciferase reporter assay. (A) Diagram of the dual-luciferase plasmid carrying the Pgr-A 5′-UTR sequence upstream of the firefly luciferase gene. The Renilla luciferase served as a control for normalization. (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for evaluating the knockdown effectiveness of siRNA targeting METTL3 in HEK293T cells. siNC, negative control. (C) Quantitative MeRIP-PCR analysis of Pgr-A 5′-UTR. (D) The effect of METTL3 knockdown on translation efficiency of the recombined dual-luciferase plasmid. (E and F) SiRNA screening to identify m6A reader proteins for the Pgr-A 5′-UTR. (E) Quantitative RT-PCR for evaluating the knockdown effectiveness of siRNAs targeting m6A reader proteins EIF3B and YTHDF1/2/3. (F) The effect of knockdown of m6A reader proteins on translation efficiency of the recombined dual-luciferase plasmid. (G and H) Point mutation analysis of m6A sites in Pgr-A 5′-UTR. (G) The location of m6A sites in the 5′-UTR of Pgr-A mRNA predicted by the SRAMP tool. Potential m6A sites are colored in red and the corresponding RRACH motifs are underlined. A-to-T mutations were introduced to abrogate each m6A site. (H) The effect of point mutations on translation efficiency of the recombined dual-luciferase plasmid. Data are presented as means ± SD. *P < 0.05.