Figure 1.
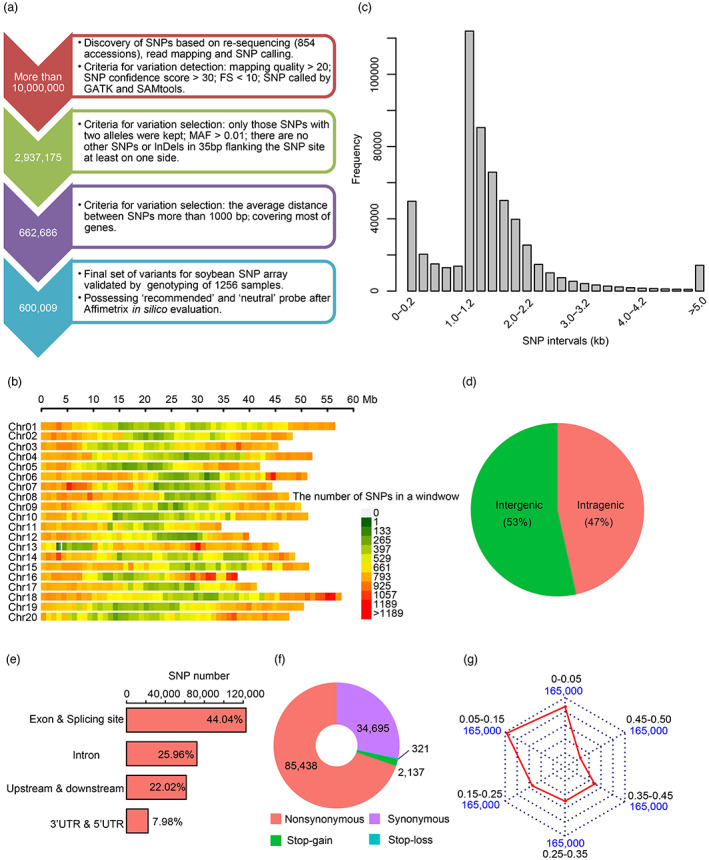
Construction of the high‐density 600K SoySNP array and its characteristics. (a) The design process of the 600K SoySNP array in soybean. MAF, minor allele frequency. (b) The distribution of SNPs along the 20 chromosomes. The number of SNPs in the non‐overlapping window with the size of 1 Mb was counted along the chromosome. (c) The distribution of SNP intervals. (d) The proportions of SNPs in intergenic and intragenic regions. (e) The classification of SNPs in intragenic regions. According to the genome annotation, SNPs in intragenic regions were classed in exonic regions (locating in a coding exon), splicing sites (within 2 bp of a splicing junction), 5′ untranslated regions (UTRs) and 3′ UTRs, intronic regions (overlapping with an intron), upstream (within a 1 kb region upstream from the transcription start site) and downstream regions (locating in a 1 kb region downstream from the transcription termination site). (f) Impacts of high‐quality SNPs in coding regions. (g) The distribution of SNPs with different minor allele frequency (MAF) in the natural soybean populations. Red lines represent the number of SNPs in various intervals for MAF.
