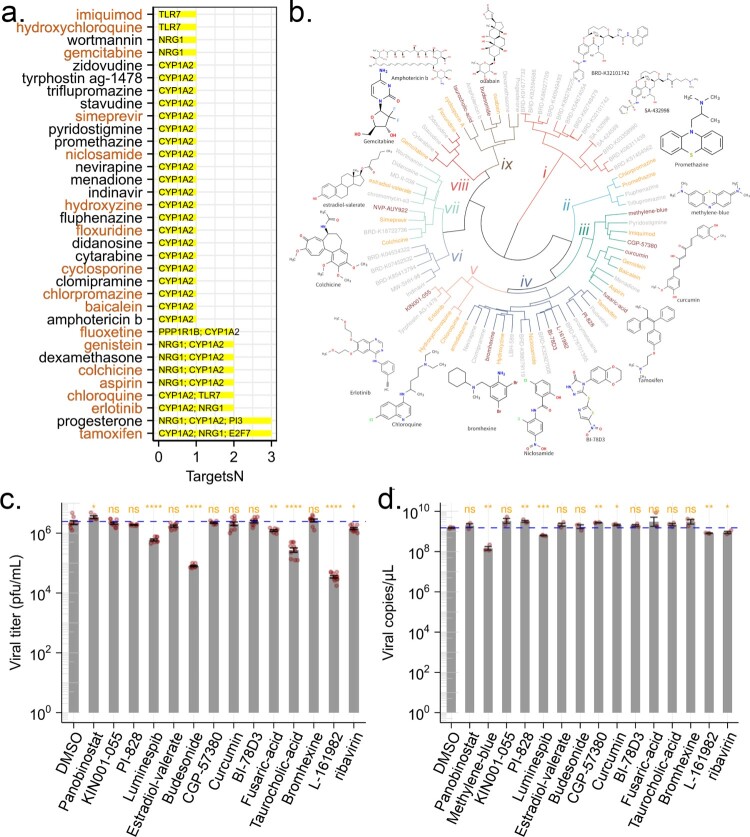
Figure 5.
Predicted anti-ZIKV agents and their effect on viral infection. (a) Candidate drugs that target TVC7. Drug candidates against TVC7 were identified by cross-referencing with DGIdb. Drugs targeted more than two genes in TVC7 or retrieved from the PubChem database as potential antiviral agents were shown. Red fonts indicated known anti-ZIKV agents. (b) Chemical structure similarity clustering of drugs identified by signature-based drug repositioning (top 40) and cross-reference with DGIdb. Different coloured branches indicated compounds with distinct chemical structures. Genes with orange colours represent known anti-ZIKV agents, darkred represents compounds being tested in this work, and grey represents others identified here. (c) and (d), ZIKV infectious titres and RNA levels in the culture supernatant of HBMECs at 48 h post-infection with ZIKV at MOI 1 and treated with the indicated compounds, 20 μM Ribavirin, or equivalent volumes of the solvents DMSO. DMSO served as a negative control for all compounds. ZIKV RNA levels were measured by RT-qPCR. ZIKV titres were measured by plaque assay. Data were analysed with student’s t-test, (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.001). Bars represent the mean ± SD of three biological replicates.