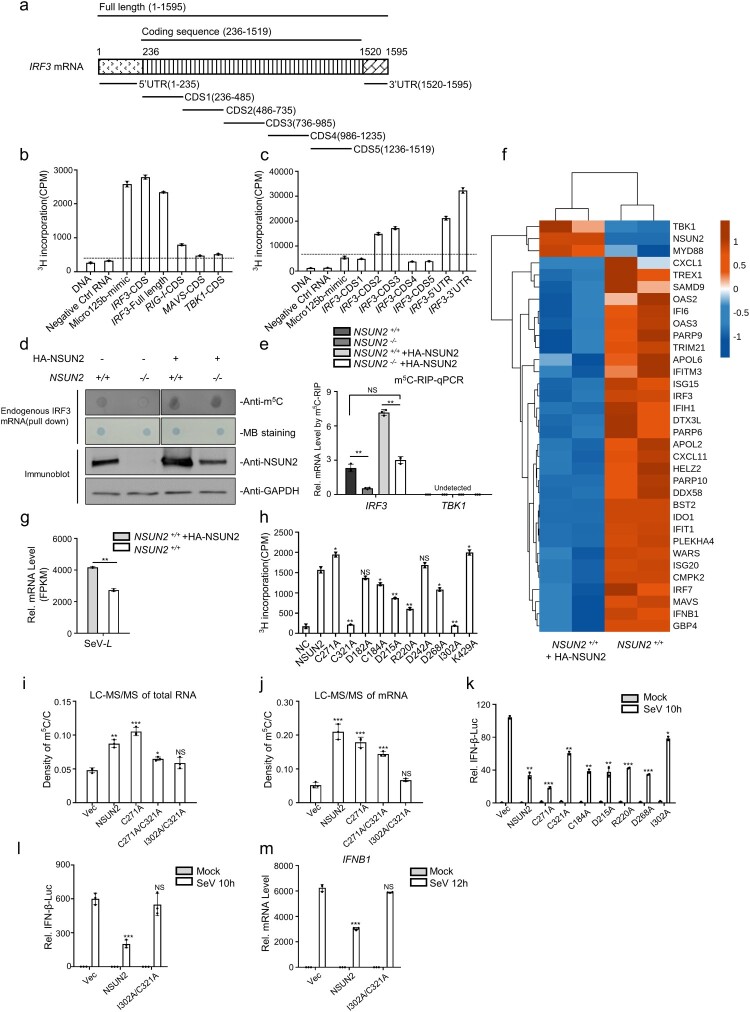
Figure 4.
NSUN2 catalyzes the formation of m5C methylation of IRF3 mRNA both exogenously and endogenously. (a) Schematic diagram of the IRF3 mRNA segments used for in vitro methylation assays and bisulfite RNA sequencing. (b) In vitro m5C methylation assays using recombinant GST-NSUN2 and the in vitro transcripts. (c) In vitro m5C methylation assays using recombinant GST-NSUN2 and the in vitro transcribed segments of IRF3 mRNA depicted in Figure 4(a). (d) m5C dot blot analysis of endogenous IRF3 mRNA (200 ng) pulled down by IRF3 CHIRP probes in wild-type HEK293T cells or NSUN2−/− HEK293T cells with or without exogenous NSUN2 overexpression. Equal IRF3 mRNAs were also loaded and verified by methylene blue (MB) staining. (e) The m5C-RIP-qPCR analysis of the m5C methylated IRF3 mRNA immunoprecipitated by m5C antibody from wild-type HEK293T cells or NSUN2−/− HEK293T cells, with or without exogenous NSUN2 expression. TBK1 was used as a negative control. (f-g) RNA-seq of HEK293T cells or HEK293T cells with NSUN2 overexpression, with infection by SeV. The heatmap (f) shows the expression levels of ISGs and several signalling molecules. The genes that we focus on are labelled with asterisks. The column diagram (g) shows the SeV replication levels. (h) In vitro m5C methylation assays using recombinant GST-NSUN2 and different mutant proteins.