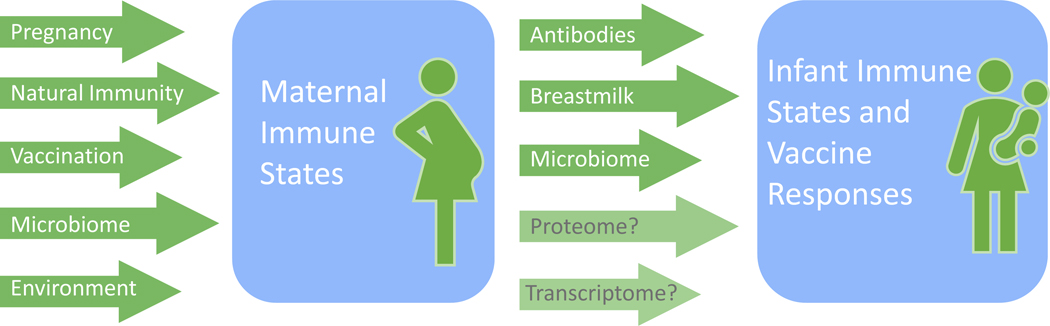
Figure 2. Determinants of maternal and infant immune states and vaccine responses.
Maternal immune states and vaccine responses can be influenced by the immunomodulation that occurs during pregnancy, by changes in microbiome composition, by exposure to pathogens which may result in maternal disease or naturally-acquired immunity, and by multiple other environmental factors. Maternal determinant such as placentally acquired antibodies, immune components of breastmilk, microbiome, as well as complex interactions at the proteomic and transcriptomic levels can also influence infant immune states and vaccine responses.