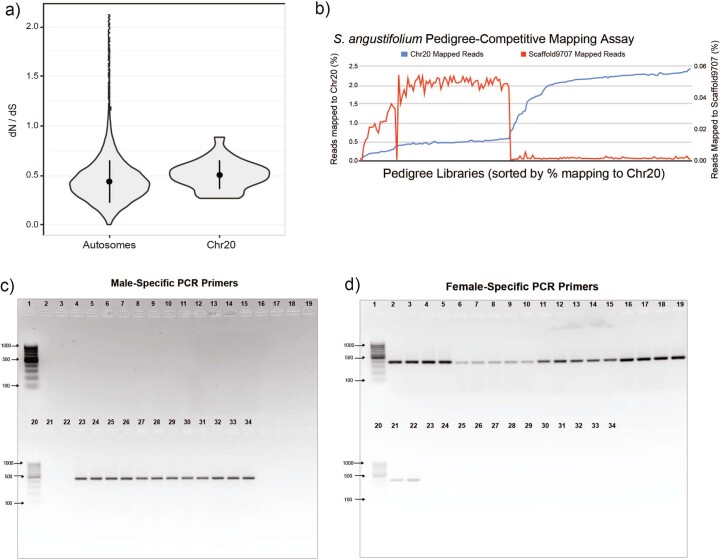
Extended Data Fig. 3. Analysis of Chr20 as a sex chromosome.
a) Violin plot depicting gene-wide rate ratios of non-synonymous (dN) to synonymous (dS) substitution for genes on autosomes (n = 1,425) and chr.20 (n = 30) across the Sphagnum diversity panel. Higher values of dN/dS in genes on chr.20 suggest relaxation in the strength of purifying selection, positive selection, or a combination of both positive and relaxed purifying selection as compared to autosomal genes. Dots and bars represent mean values ± one standard deviation, respectively. b) S. angustifolium pedigree competitive mapping assay. Reads from each pedigree library were mapped to the genome assembly of S.angustifolium, along with the scaffold sequence Scaffold9707. Reads mapped to chr. 20 and Scaffold9707 are expressed as the total percentage per reads within the fastq file. c and d) Polymerase chain reaction results of male-specific (panel c) and female specific (panel d) primers used for amplification with Sphagnum samples of known sex (metadata details provided in Supplementary Table 12), Expected amplicon size for the PCR reaction is 444 bp (panel c) and 394 bp (panel d). PCR amplicons were separated on a 2% agarose gel, run for 2 hours at 80 volts. GeneRuler DNA ladder was run in lanes 1 and 20. DNA from female Sphagnum samples were loaded into lanes 2–19;21–22 and DNA from males was loaded into lanes 23–34. Individual gel results were not replicated but were independently consistent (for example male samples were 100% positive for male specific primers (panel c) and 100% negative for female-specific primers (panel d).