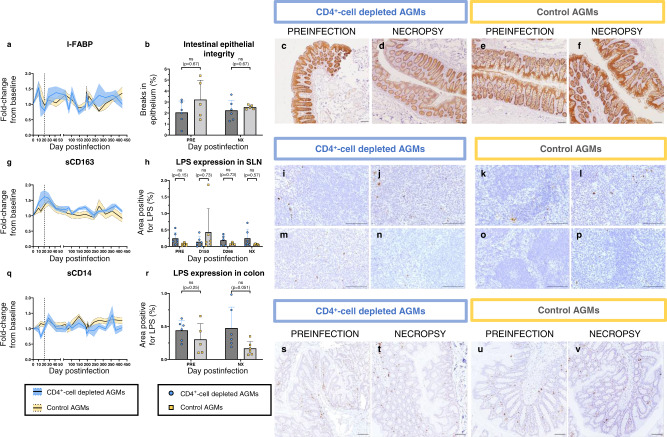
Fig. 8. Monitoring of gut integrity and microbial translocation.
Assessment of gut integrity was performed by monitoring a marker of gut damage in plasma, intestinal fatty acid binding protein (I-FABP) (a), and the expression of a tight-junction protein, claudin-3 (b–f), by immunohistochemistry (IHC) in CD4+-cell-depleted AGMs (blue) and controls (yellow). Assessment of microbial translocation was performed by monitoring two soluble markers of monocyte activation, soluble CD163 (sCD163) (g) and soluble CD14 (sCD14) (q), that are associated with microbial translocation and disease progression. Microbial translocation was also monitored by quantifying the expression of lipopolysaccharide (LPS, brown) in sLNs (h–p) and in colon tissues (r–v), by IHC. For IHC, images are representative of n = 6 animals in each group, with at least 20 images taken per animal for colon tissues and at least 9 images for sLNs. For all images, the scale bar represents 100 μm. Data presented are means and standard deviations of the means for ELISA (a, g, q), and means and standard deviations for IHC (b, h, r) (n = 6 AGMs for CD4+-cell-depleted AGMs and controls, except for (b) and (r) for which n = 5 AGMs for controls at baseline). Data in (b), (h) and (r) were analyzed with unpaired, two-sided, nonparametric Mann–Whitney tests, followed by Holm-Šídák’s correction for multiple comparisons. AGMs African Green Monkeys, sLNs superficial lymph nodes, LPS lipopolysaccharide, ns not significant, NX necropsy, PRE preinfection.