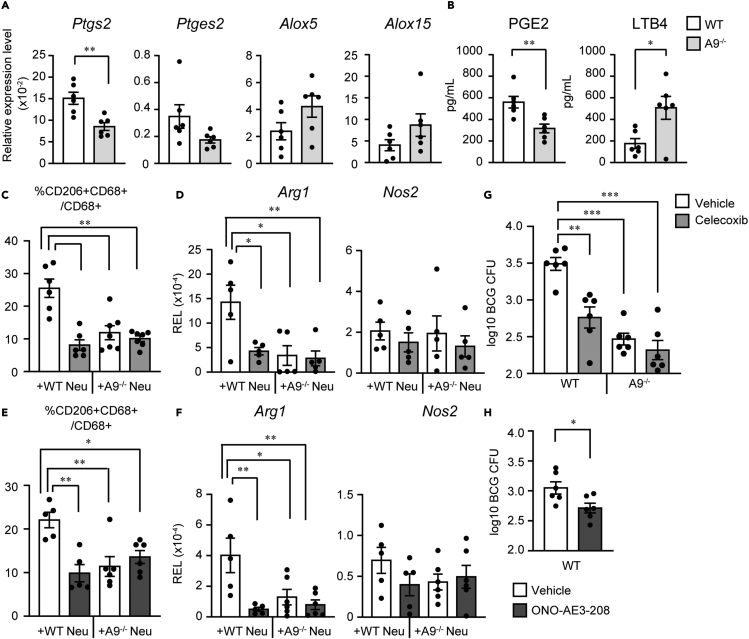
Figure 4.
Neutrophil A9-dependent COX-2 induction for macrophage M2 polarization
(A) Relative expression levels of Ptgs2, Ptges2, Alox5, and Alox15 mRNA from BCG-elicited WT or A9−/− neutrophils were measured via the delta CT method and normalized to β2m expression levels.
(B) Amount of PGE2 or LTB4 in the 18-h culture supernatant of BCG-elicited neutrophils from WT and A9−/− mice.
(C) Percentage of CD206+ cells among CD68+ total macrophages from BMMs co-cultured with Neu pre-treated with the COX-2-specific inhibitor celecoxib.
(D) mRNA Expression of Arg1 and Nos2 in BMMs co-cultured with celecoxib-treated Neu was analyzed via quantitative real-time PCR.
(E) Percentage of CD206+ cells among CD68+ total macrophages from WT BMMs treated with or without EP antagonist ONO-AE3-208 before the addition of Neu.
(F) Arg1 and Nos2 mRNA induction in BMMs, as indicated in (E), was analyzed via quantitative real-time PCR.
(G) CFU of BCG in the peritoneal macrophages of WT or A9−/− mice treated with celecoxib (light gray) or vehicle (open) at 1 week after BCG infection is shown.
(H) CFU of BCG in the peritoneal macrophages of ONO-AE3-208-treated (dark gray) and vehicle-treated (open) WT mice is shown. Data were pooled from two independent experiments with three mice per experimental group (A, B, G, and H). Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ∗∗∗p < 0.0005, ∗∗p < 0.005, ∗p < 0.05, Welch’s t-test (A, B, G, and H) or ANOVA and post hoc Tukey-Kramer test (C–F).