Figure 3.
Perinatal exposure to MeHg increases the genesis of deep layer cortical neurons in vivo
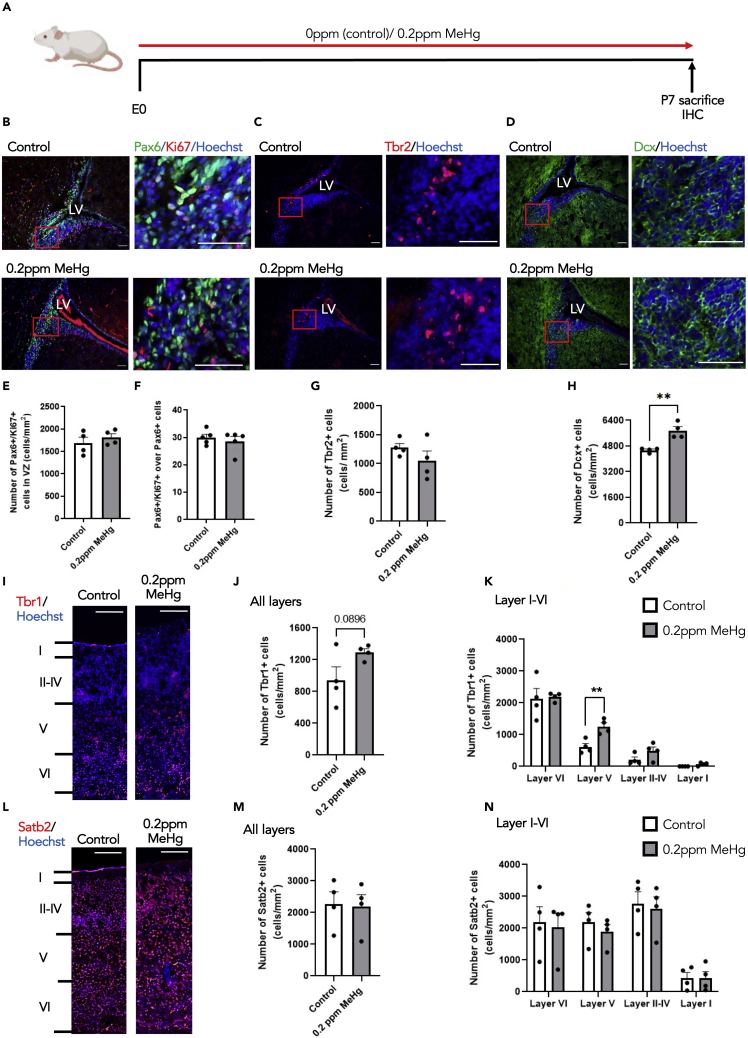
(A) Schematic of perinatal exposure to MeHg in pregnant mice, created with BioRender.com. 0ppm (control) and 0.2ppm MeHg were administered through drinking water to pregnant mice starting at E0 until P7. At P7 brains were collected for immunohistochemistry.
(B–D) Images of P7 SVZ sections from pups receiving 0 and 0.2ppm MeHg treatment since E0, immunostained for Pax6 (B, green), Ki67 (B, red), Tbr2 (C, red) and DCX (D, green) and counterstained for Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm.
(E–H) Quantitative analysis of the number and proportion of of Ki67+/Pax6+proliferating cortical precursors (E-F), the number of Tbr2+ intermediate progenitors (G) and DCX+ immature neurons (H) within SVZ of P7 brains, determined from sections similar to those shown in (B, C, D). n = 4 embryos/group, Student’s t test, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(I and L) Images of P7 cerebral cortex sections from pups receiving 0 and 0.2ppm MeHg treatment since E0, immunostained for Tbr1 (I, red) and Satb2 (L, red) and counterstained for Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 50 μm.
(J, K, M, and N) Quantitative analysis of the number of Tbr1+ deep layer neurons (J-K) and Satb2+ superficial layer mature neurons (M−N) at all cortical neuron layers (layer I-layer VI), determined from sections similar to those shown in (I, L). n = 4 embryos/group, Student’s t test, ∗∗p < 0.01. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM). See also Figure S3.