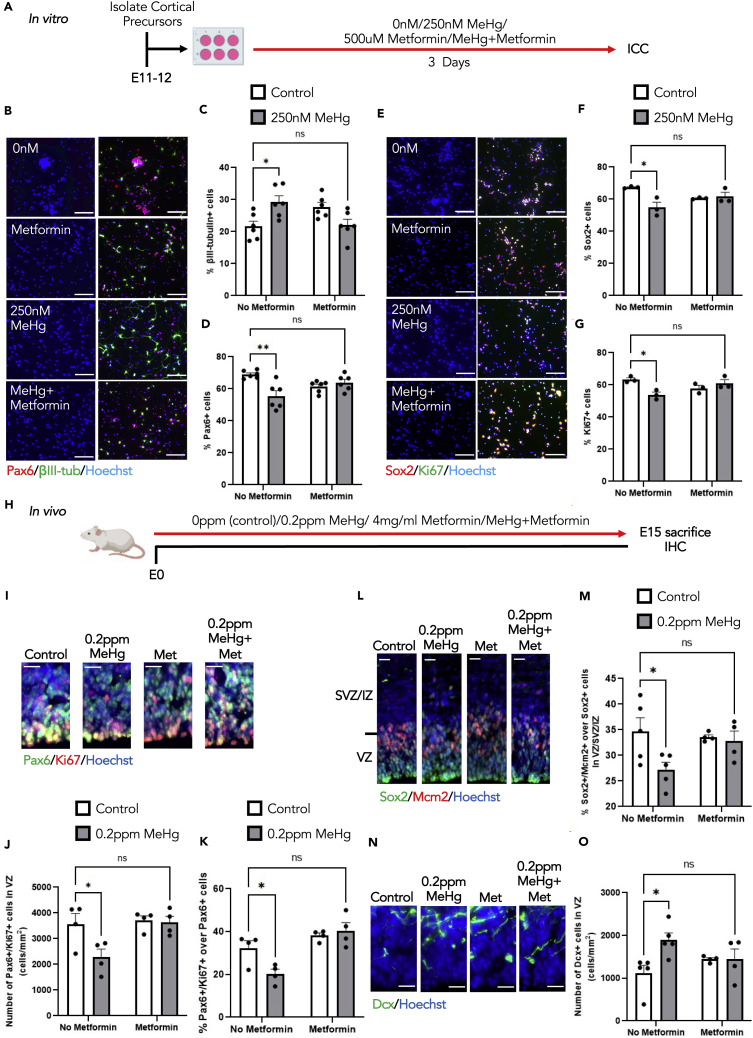
Figure 7.
Metformin eliminates premature neuronal differentiation caused by MeHg exposure
(A) Schematic of cortical percussor isolated from E11-12 CD1 mice, created with BioRender.com. Cells were exposed to four conditions: i) control (0ppm MeHg+0 μM metformin), ii) 250 nM MeHg, iii) 500 μM metformin, iv) co-treatment of 250 nM MeHg +500 μM metformin for 3 days, followed by immunocytochemical analysis.
(B and E) Images of cortical percussors after 3 days in culture treated with four conditions mentioned in (A), immunostained for Pax6 (B, red), βIII-tubulin (B, green), Ki67 (E, green), Sox2 (E, red) and counterstained for Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 30 μm.
(C) Quantitative analysis of βIII-tubulin+ cells, n = 6 independent experiments, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 20) = 15.28, p = 0.0009, group F(1, 20) = 0.3370, p = 0.5680, metformin F(1, 20) = 0.09295, p = 0.7636, n = 24).
(D) Quantitative analysis of Pax6+ cells, n = 6 independent experiments, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 20) = 13.99, p = 0.0013, group F(1, 20) = 6.652, p = 0.0179, metformin F(1, 20) = 0.04803, p = 0.8287, n = 24).
(F) Quantitative analysis of Sox2+ cells, n = 3 independent experiments, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 8) = 10.05, p = 0.0132, group F(1, 8) = 7.171, p = 0.0280, metformin F(1, 8) = 0.0002320, p = 0.9882, n = 12).
(G) Quantitative analysis of Ki67+ cells. n = 3 independent experiments, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 8) = 12.89, p = 0.0071, group F(1, 8) = 3.335, p = 0.1053, metformin F(1, 8) = 0.2942, p = 0 0.6023, n = 12) with post hoc test, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗p < 0.05, ns (non-significant).
(H) Schematic of prenatal exposure of MeHg to pregnant mice, created with BioRender.com. Pregnant mice were exposed to four conditions: i) control (0ppm MeHg + 0 mg metformin, ii) 0.2ppm MeHg, iii) 4 mg/ml metformin, iv) 0.2ppm MeHg + 4 mg/mL metformin. Treatment was administered through drinking water to pregnant mice starting at E0 until E15. At E15 brains were collected for immunohistochemistry.
(I, L, N) Images of E15 cerebral cortex sections from embryos receiving four condition treatments mentioned in (H), immunostained for Pax6 (I, green), Ki67 (I, red) or Sox2 (L, green), Mcm2 (L, red), or DCX (N, green) and counterstained for Hoechst (blue). Scale bar: 20 μm.
(J and K) Quantitative analysis of the number and proportion of Pax6+/Ki67+ proliferating cortical precursors in the VZ. J: two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 12) = 4.060, p = 0.0669, group F(1, 12) = 5.253, p = 0.0408, metformin F(1, 12) = 6.156, p = 0.0289, n = 16). K: two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 12) = 6.461, p = 0.0259, group F(1, 12) = 2.961, p = 0.1109, metformin F(1, 12) = 20.79, p = 0.0007, n = 16) with post hoc test, ∗p < 0.05, ns (non-significant).
(M) Quantitative analysis of the number of Sox2+/Mcm2+proliferating radial glial cells within VZ and SVZ/IZ, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 14) = 3.167, p = 0.0969, group F(1, 14) = 4.683, p = 0.0482, metformin F(1, 14) = 1.379, p = 0.2599, n = 18) with post hoc test, ∗p < 0.05, ns (non-significant).
(O) Quantitative analysis of the number of DCX+ cells in the VZ, two-way ANOVA(group × metformin interaction F(1, 14) = 4.817, p = 0.0455, group F(1, 14) = 4.858, p = 0.0448, metformin F(1, 14) = 0.1290, p = 0.7248, n = 18) with post hoc test, ∗p < 0.05, ns (non-significant). These quantifications (J-K, M, O) were determined from cortical sections similar to those shown in (I, L, N). n = 4–5 embryos per group. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM). See also Figure S7.