Figure 6.
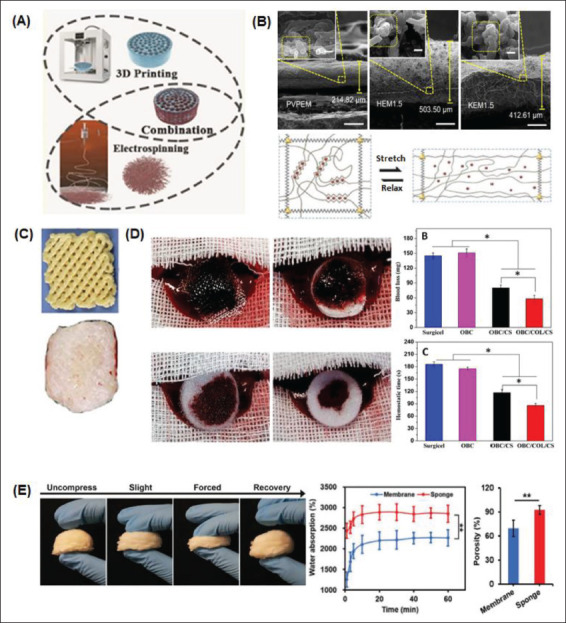
Combined methods of micro/nanosurface modification manufacture for rapid hemostasis. (A) 3D/4D printing and electrospinning techniques can be combined to achieve beneficial micro/nanosurface manipulations in hemostat fabrication[154]. (B) SEM images of electrospun nanoclay membranes: polyvinylpyrrolidone electrospun membrane (PVPEM), halloysite electrospun membrane (HEM), and kaolinite electrospun membrane (KEM)[14,41]. (C) Advanced fabrication for electrospun 3D nanofiber aerogels and scaffolds[94]. (D) Macroscopic images and subsequent evaluation of the hemostatic capacity of different electrospun sponges[107]. (E) A nanofiber sponge undergoing different degrees of compression. Water absorption and porosity percentages between the sponge and a membrane are compared[7].
