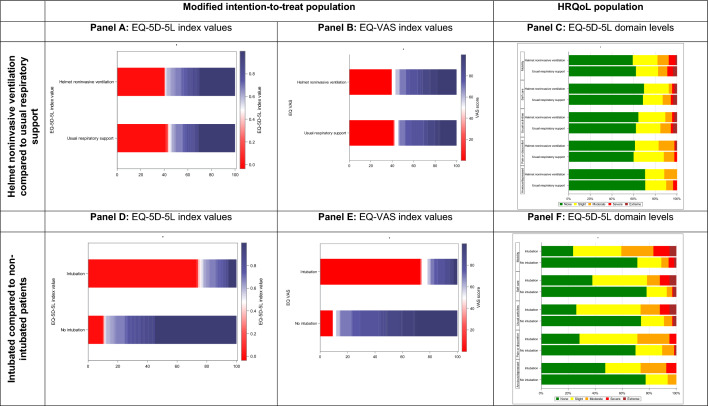
Fig. 2.
A, B and C Comparisons of EQ-5D-5L index values, EQ-VAS and EQ-5D-5L dimension levels between patients in the helmet noninvasive ventilation and usual respiratory support groups; none of the comparisons were statistically significantly different between the two groups. A and B Distribution of the EQ-5D-5L index values and EQ-VAS as horizontally stacked proportions in patients assigned to helmet noninvasive ventilation and usual respiratory support in the modified intention-to-treat population. C Distributions of individual EQ-5D-5L dimension levels in the HRQoL population in patients assigned to helmet noninvasive ventilation and usual respiratory support (see also Table S6, Online Supplement). D, E and F Comparisons of EQ-5D-5L index values, EQ-VAS and EQ-5D-5L dimension levels between patients who were intubated and those who were not intubated; all comparisons were statistically significantly different between the two groups. D and E Distribution of the EQ-5D-5L index values and EQ-VAS as horizontally stacked proportions in patients who were intubated and those who were not intubated in the modified intention-to-treat population. F Distributions of individual EQ-5D-5L dimension levels in patients who were intubated and those who were not in the HRQoL population (see also Tables S8 and S9, Online Supplement)