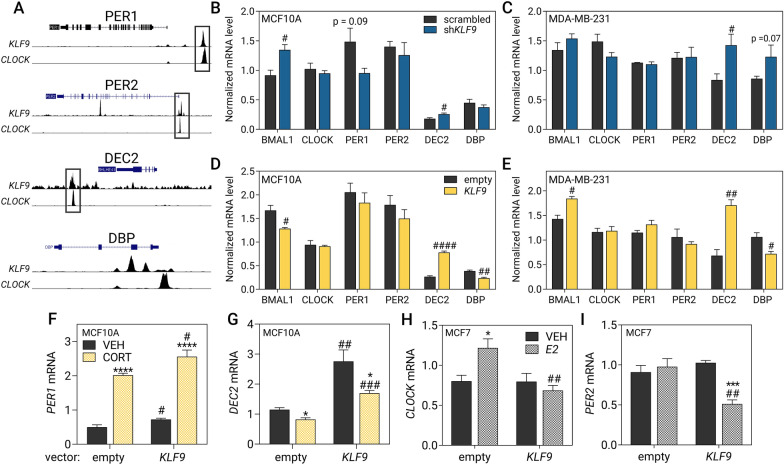
Fig. 4.
KLF9 influences the hormone response of some clock genes. A Publicly available KLF9 and CLOCK ChIP-seq data in MCF7 cells [47] were visualized using the UCSC genome browser [50] mapped to the human GRCh37/hg19 genome assembly. In black-outlined boxes are KLF9 peaks which often co-localize with CLOCK. Effects of KLF9 B, C knockdown and D, E overexpression induced moderate changes on the expression the clock genes BMAL1, CLOCK, PER1, PER2, DEC2, and DBP in B, D MCF10A and C, E MDA-MB-231 cells as measured through RT-qPCR. F, G MCF10A cells overexpressing KLF9 were treated with 100 nM CORT for 2 h prior to analysis of gene expression through RT-qPCR. KLF9 overexpression augmented the F upregulation of PER1 (two-way ANOVA; treatment: P < 0.0001; overexpression: P = 0.0027) and G repression of DEC2 mRNA upon CORT treatment (two-way ANOVA; treatment: P = 0.0009; overexpression: P < 0.0001). H, I MCF7 cells overexpressing KLF9 were treated with 1 μM E2 for 24 h prior to analysis of gene expression through RT-qPCR. Ectopic expression of KLF9 abrogated the induction of H CLOCK (two-way ANOVA; treatment: P = 0.2205; Overexpression: P = 0.0153) and reduced PER2 transcript in E2-treated cells (two-way ANOVA; Treatment: P = 0.0049; Overexpression: P = 0.0165). Bars represent mean ± SEM with statistically significant differences determined through two-way ANOVA for main effects of treatment or overexpression and Student’s t-test for individual effects of hormone treatment (*) and knockdown or overexpression (#). All experiments were performed with N ≥ 3 replicates